Objective napping, cognitive decline, and risk of cognitive impairment in older men
- PMID: 31227429
- PMCID: PMC6699896
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jalz.2019.04.009
Objective napping, cognitive decline, and risk of cognitive impairment in older men
Abstract
Introduction: Little is known about the longitudinal association between napping and cognitive impairment in older adults.
Methods: We used wrist actigraphy to measure naps in 2751 community-dwelling older men. Cognition was assessed repeatedly over 12 years, and clinically significant cognitive impairment was determined by physician diagnosis, Alzheimer's medication use or a significant cognitive decline.
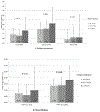
Results: After adjustment for all covariates, men with longer napping duration had greater cognitive decline and higher risk of cognitive impairment. Men who napped for ≥120 min/day (vs. <30 min/day) were 66% more likely to develop cognitive impairment (odds ratio = 1.66, 95% CI: 1.09-2.54) in 12 years. Further adjustment for nighttime sleep quality did not appreciably alter the results. The association between napping and cognitive impairment was more pronounced among those with higher sleep efficiency and average sleep duration.
Discussion: Napping might be useful as an early marker of cognitive impairment in the elderly, and its cognitive effects may differ by nighttime sleep.
Keywords: Cognitive decline; Cognitive impairment; Daytime sleepiness; Dementia; Epidemiology; Longitudinal study; Napping; Sleep.
Copyright © 2019 the Alzheimer's Association. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Foley DJ, Vitiello MV, Bliwise DL, et al.: Frequent napping is associated with excessive daytime sleepiness, depression, pain, and nocturia in older adults: findings from the National Sleep Foundation ‘2003 Sleep in America’ Poll. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 2007; 15:344–350 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- K24 AG031155/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG042145/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070842/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071194/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG042143/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG042139/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070837/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000128/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070838/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR066160/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070839/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG042168/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG042124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AG056598/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070848/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070841/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG042140/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG027810/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070847/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States

