HDAC Inhibition Enhances the In Vivo Efficacy of MEK Inhibitor Therapy in Uveal Melanoma
- PMID: 31227503
- PMCID: PMC6744978
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-3382
HDAC Inhibition Enhances the In Vivo Efficacy of MEK Inhibitor Therapy in Uveal Melanoma
Abstract
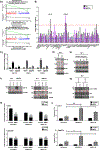
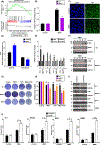
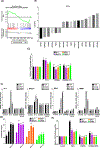
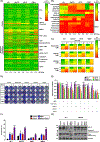
Purpose: The clinical use of MEK inhibitors in uveal melanoma is limited by the rapid acquisition of resistance. This study has used multiomics approaches and drug screens to identify the pan-HDAC inhibitor panobinostat as an effective strategy to limit MEK inhibitor resistance.Experimental Design: Mass spectrometry-based proteomics and RNA-Seq were used to identify the signaling pathways involved in the escape of uveal melanoma cells from MEK inhibitor therapy. Mechanistic studies were performed to evaluate the escape pathways identified, and the efficacy of the MEK-HDAC inhibitor combination was demonstrated in multiple in vivo models of uveal melanoma.
Results: We identified a number of putative escape pathways that were upregulated following MEK inhibition, including the PI3K/AKT pathway, ROR1/2, and IGF-1R signaling. MEK inhibition was also associated with increased GPCR expression, particularly the endothelin B receptor, and this contributed to therapeutic escape through ET-3-mediated YAP signaling. A screen of 289 clinical grade compounds identified HDAC inhibitors as potential candidates that suppressed the adaptive YAP and AKT signaling that followed MEK inhibition. In vivo, the MEK-HDAC inhibitor combination outperformed either agent alone, leading to a long-term decrease of tumor growth in both subcutaneous and liver metastasis models and the suppression of adaptive PI3K/AKT and YAP signaling.
Conclusions: Together, our studies have identified GPCR-mediated YAP activation and RTK-driven AKT signaling as key pathways involved in the escape of uveal melanoma cells from MEK inhibition. We further demonstrate that HDAC inhibition is a promising combination partner for MEK inhibitors in advanced uveal melanoma.
©2019 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Co-targeting HGF/cMET Signaling with MEK Inhibitors in Metastatic Uveal Melanoma.Mol Cancer Ther. 2017 Mar;16(3):516-528. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0552. Epub 2017 Jan 30. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017. PMID: 28138035 Free PMC article.
-
Paracrine Effect of NRG1 and HGF Drives Resistance to MEK Inhibitors in Metastatic Uveal Melanoma.Cancer Res. 2015 Jul 1;75(13):2737-48. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-0370. Epub 2015 May 7. Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25952648 Free PMC article.
-
Combination small molecule MEK and PI3K inhibition enhances uveal melanoma cell death in a mutant GNAQ- and GNA11-dependent manner.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Aug 15;18(16):4345-55. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-3227. Epub 2012 Jun 25. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22733540 Free PMC article.
-
How to MEK the best of uveal melanoma: A systematic review on the efficacy and safety of MEK inhibitors in metastatic or unresectable uveal melanoma.Eur J Cancer. 2018 Nov;103:41-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2018.08.005. Epub 2018 Sep 8. Eur J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30205280
-
The Role of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in Uveal Melanoma: Current Evidence.Anticancer Res. 2018 Jul;38(7):3817-3824. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.12665. Anticancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29970501 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of targetable epigenetic vulnerabilities for uveal melanoma.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 25:2024.10.11.617464. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.11.617464. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39416076 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
A New Player in Neuroblastoma: YAP and Its Role in the Neuroblastoma Microenvironment.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Sep 16;13(18):4650. doi: 10.3390/cancers13184650. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34572875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uveal melanoma: progress in molecular biology and therapeutics.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2020 Oct 22;12:1758835920965852. doi: 10.1177/1758835920965852. eCollection 2020. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33149769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decitabine limits escape from MEK inhibition in uveal melanoma.Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2020 May;33(3):507-514. doi: 10.1111/pcmr.12849. Epub 2019 Dec 6. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2020. PMID: 31758842 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Fibroblast Growth Factors in the Crosstalk of Hepatic Stellate Cells and Uveal Melanoma Cells in the Liver Metastatic Niche.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 29;23(19):11524. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911524. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goldsmith Z, Dhanasekaran D. G protein regulation of MAPK networks. Oncogene. 2007;26:3122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

