Acculturation drives the evolution of intergroup conflict
- PMID: 31227610
- PMCID: PMC6628825
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1810404116
Acculturation drives the evolution of intergroup conflict
Abstract
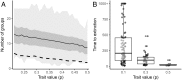
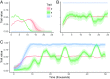
Conflict between groups of individuals is a prevalent feature in human societies. A common theoretical explanation for intergroup conflict is that it provides benefits to individuals within groups in the form of reproduction-enhancing resources, such as food, territory, or mates. However, it is not always the case that conflict results from resource scarcity. Here, we show that intergroup conflict can evolve, despite not providing any benefits to individuals or their groups. The mechanism underlying this process is acculturation: the adoption, through coercion or imitation, of the victor's cultural traits. Acculturation acts as a cultural driver (in analogy to meiotic drivers) favoring the transmission of conflict, despite a potential cost to both the host group as a whole and to individuals in that group. We illustrate this process with a two-level model incorporating state-dependent event rates and evolving traits for both individuals and groups. Individuals can become "warriors" who specialize in intergroup conflicts, but are costly otherwise. Additionally, groups are characterized by cultural traits, such as their tendency to engage in conflict with other groups and their tendency for acculturation. We show that, if groups engage in conflicts, group selection will favor the production of warriors. Then, we show that group engagement can evolve if it is associated with acculturation. Finally, we study the coevolution of engagement and acculturation. Our model shows that horizontal transmission of culture between interacting groups can act as a cultural driver and lead to the maintenance of costly behaviors by both individuals and groups.
Keywords: cultural evolution; group selection; intergroup conflict.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
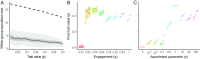
References
-
- Keeley L. H., War Before Civilization (Oxford Univ Press, New York, NY, 1996).
-
- Otterbein K. F., How War Began (Texas A&M Univ Press, College Station, TX, 2004).
-
- Bowles S., Did warfare among ancestral hunter-gatherers affect the evolution of human social behaviors? Science 324, 1293–1298 (2009). - PubMed
-
- van der Dennen J. M. G., The Origin of War: The Evolution of a Male-Coalitional Reproductive Strategy (Origin, Groningen, Netherlands, 1995).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

