Pharmacokinetics, Biodistribution, and Anti-Angiogenesis Efficacy of Diamino Propane Tetraiodothyroacetic Acid-conjugated Biodegradable Polymeric Nanoparticle
- PMID: 31227723
- PMCID: PMC6588584
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-44979-6
Pharmacokinetics, Biodistribution, and Anti-Angiogenesis Efficacy of Diamino Propane Tetraiodothyroacetic Acid-conjugated Biodegradable Polymeric Nanoparticle
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note: Pharmacokinetics, Biodistribution, and Anti-Angiogenesis Efficacy of Diamino Propane Tetraiodothyroacetic Acid-conjugated Biodegradable Polymeric Nanoparticle.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 3;13(1):16594. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-43642-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37789122 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
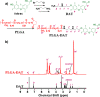
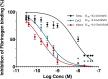
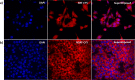
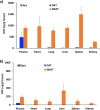
The anti-angiogenic agent, diamino propane tetraiodothyroacetic acid (DAT), is a thyro-integrin (integrin αvβ3) antagonist anticancer agent that works via genetic and nongenetic actions. Tetraiodothyroacetic acid (tetrac) and DAT as thyroid hormone derivatives influence gene expression after they transport across cellular membranes. To restrict the action of DAT to the integrin αvβ3 receptors on the cell surface, we used DAT-conjugated PLGA nanoparticles (NDAT) in an active targeting mode to bind to these receptors. Preparation and characterization of NDAT is described, and both in vitro and in vivo experiments were done to compare DAT to NDAT. Intracellular uptake and distribution of DAT and NDAT in U87 glioblastoma cells were evaluated using confocal microscopy and showed that DAT reached the nucleus, but NDAT was restricted from the nucleus. Pharmacokinetic studies using LC-MS/MS analysis in male C57BL/6 mice showed that administration of NDAT improved the area under the drug concentration curve AUC(0-48 h) by 4-fold at a dose of 3 mg/kg when compared with DAT, and Cmax of NDAT (4363 ng/mL) was 8-fold greater than that of DAT (548 ng/mL). Biodistribution studies in the mice showed that the concentrations of NDAT were higher than DAT/Cremophor EL micelles in heart, lung, liver, spleen, and kidney. In another mouse model using female NCr nude homozygous mice with U87 xenografts, tumor growth was significantly decreased at doses of 1 and 3 mg/kg of NDAT. In the chick chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) assay used to measure angiogenesis, DAT (500 ng/CAM) resulted in 48% inhibition of angiogenesis levels. In comparison, NDAT at low dose (50 ng/CAM) showed 45% inhibition of angiogenesis levels. Our investigation of NDAT bridges the study of polymeric nanoparticles and anti-angiogenic agents and offers new insight for the rational design of anti-angiogenic agents.
Conflict of interest statement
S.A.M. holds stock in NanoPharmaceuticals LLC, which is developing anticancer drugs. K.A.K. is a paid consultant of NanoPharmaceuticals LLC. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Nanoparticulate Tetrac Inhibits Growth and Vascularity of Glioblastoma Xenografts.Horm Cancer. 2017 Jun;8(3):157-165. doi: 10.1007/s12672-017-0293-6. Epub 2017 Apr 10. Horm Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28396979 Free PMC article.
-
Tetraidothyroacetic acid (tetrac) and tetrac nanoparticles inhibit growth of human renal cell carcinoma xenografts.Anticancer Res. 2009 Oct;29(10):3825-31. Anticancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19846915
-
Tetraiodothyroacetic acid (tetrac) and nanoparticulate tetrac arrest growth of medullary carcinoma of the thyroid.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Apr;95(4):1972-80. doi: 10.1210/jc.2009-1926. Epub 2010 Feb 4. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 20133461
-
Tetrac as an anti-angiogenic agent in cancer.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2019 Jun 1;26(6):R287-R304. doi: 10.1530/ERC-19-0058. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31063970 Review.
-
Actions of L-thyroxine (T4) and Tetraiodothyroacetic Acid (Tetrac) on Gene Expression in Thyroid Cancer Cells.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jul 7;11(7):755. doi: 10.3390/genes11070755. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32645835 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of novel thyrointegrin αvβ3 antagonist fb-PMT (NP751) in the management of human glioblastoma multiforme.Neurooncol Adv. 2022 Dec 8;5(1):vdac180. doi: 10.1093/noajnl/vdac180. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. Neurooncol Adv. 2022. PMID: 36879662 Free PMC article.
-
αvβ3 Integrin Antagonists Enhance Chemotherapy Response in an Orthotopic Pancreatic Cancer Model.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Feb 27;11:95. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00095. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32174830 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Cancer Activities of Thyrointegrin αvβ3 Antagonist Mono- and Bis-Triazole Tetraiodothyroacetic Acid Conjugated via Polyethylene Glycols in Glioblastoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 3;13(11):2780. doi: 10.3390/cancers13112780. Cancers (Basel). 2021. Retraction in: Cancers (Basel). 2024 May 15;16(10):1880. doi: 10.3390/cancers16101880. PMID: 34204997 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Emerging trends in the nanomedicine applications of functionalized magnetic nanoparticles as novel therapies for acute and chronic diseases.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Aug 31;20(1):393. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01595-3. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 36045375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anticancer Efficacy and Mechanisms of a Dual Targeting of Norepinephrine Transporter and Thyrointegrin αvβ3 Antagonist in Neuroblastoma.J Cancer. 2022 May 16;13(8):2594-2606. doi: 10.7150/jca.72522. eCollection 2022. J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35711848 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mousa, S. A. & Davis, P. J. In Angiogenesis Modulations in Health and Disease (eds Mousa, S.A. & Davis, P.J.) (Springer, 2013).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

