Awareness of Stroke Signs and Symptoms and Calling 9-1-1 Among US Adults: National Health Interview Survey, 2009 and 2014
- PMID: 31228234
- PMCID: PMC6638588
- DOI: 10.5888/pcd16.180564
Awareness of Stroke Signs and Symptoms and Calling 9-1-1 Among US Adults: National Health Interview Survey, 2009 and 2014
Abstract
Introduction: Early recognition of stroke symptoms and recognizing the importance of calling 9-1-1 improves the timeliness of appropriate emergency care, resulting in improved health outcomes. The objective of this study was to assess changes in awareness of stroke symptoms and calling 9-1-1 from 2009 to 2014.
Methods: We analyzed data among 27,211 adults from 2009 and 35,862 adults from 2014 using the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS). The NHIS included 5 questions in both 2009 and 2014 about stroke signs and symptoms and one about the first action to take when someone is having a stroke. We estimated the prevalence of awareness of each symptom, all 5 symptoms, the importance of calling 9-1-1, and knowledge of all 5 symptoms plus the importance of calling 9-1-1 (indicating recommended stroke knowledge). We assessed changes from 2009 to 2014 in the prevalence of awareness. Data analyses were conducted in 2016.
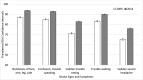
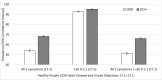
Results: In 2014, awareness of stroke symptoms ranged from 76.1% (sudden severe headache) to 93.7% (numbness of face, arm, leg, side); 68.3% of respondents recognized all 5 symptoms, and 66.2% were aware of all recommended stroke knowledge. After adjusting for sex, age, educational attainment, and race/ethnicity, logistic regression results showed a significant absolute increase of 14.7 percentage points in recommended stroke knowledge from 2009 (51.5%) to 2014 (66.2%). Among US adults, recommended stroke knowledge increased from 2009 to 2014.
Conclusion: Stroke awareness among US adults has improved but remains suboptimal.
Figures
References
-
- Benjamin EJ, Blaha MJ, Chiuve SE, Cushman M, Das SR, Deo R, et al.; American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics — 2017 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017;135(10):e146–603. 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000485 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Morimoto A, Miyamatsu N, Okamura T, Nakayama H, Toyoda K, Suzuki K, et al. Effects of intensive and moderate public education on knowledge of early stroke symptoms among a Japanese population: the Acquisition of Stroke Knowledge study. Stroke 2013;44(10):2829–34. 10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.001537 - DOI - PubMed
-
- UAB Research. Is IRB review required for use of public datasets? https://www.uab.edu/research/administration/offices/IRB/FAQs/Pages/Publi.... Accessed April 10, 2019.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

