A machine learning investigation of volumetric and functional MRI abnormalities in adults born preterm
- PMID: 31228329
- PMCID: PMC6865380
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.24698
A machine learning investigation of volumetric and functional MRI abnormalities in adults born preterm
Abstract
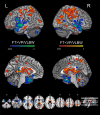
Imaging studies have characterized functional and structural brain abnormalities in adults after premature birth, but these investigations have mostly used univariate methods that do not account for hypothesized interdependencies between brain regions or quantify accuracy in identifying individuals. To overcome these limitations, we used multivariate machine learning to identify gray matter volume (GMV) and amplitude of low frequency fluctuations (ALFF) brain patterns that best classify young adults born very preterm/very low birth weight (VP/VLBW; n = 94) from those born full-term (FT; n = 92). We then compared the spatial maps of the structural and functional brain signatures and validated them by assessing associations with clinical birth history and basic cognitive variables. Premature birth could be predicted with a balanced accuracy of 80.7% using GMV and 77.4% using ALFF. GMV predictions were mediated by a pattern of subcortical and middle temporal reductions and volumetric increases of the lateral prefrontal, medial prefrontal, and superior temporal gyrus regions. ALFF predictions were characterized by a pattern including increases in the thalamus, pre- and post-central gyri, and parietal lobes, in addition to decreases in the superior temporal gyri bilaterally. Decision scores from each classification, assessing the degree to which an individual was classified as a VP/VLBW case, were predicted by the number of days in neonatal hospitalization and birth weight. ALFF decision scores also contributed to the prediction of general IQ, which highlighted their potential clinical significance. Combined, the results clarified previous research and suggested that primary subcortical and temporal damage may be accompanied by disrupted neurodevelopment of the cortex.
Keywords: ALFF; VBM; machine learning; multivariate; premature birth; resting-state fMRI.
© 2019 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Decreased BOLD fluctuations in lateral temporal cortices of premature born adults.Hum Brain Mapp. 2018 Dec;39(12):4903-4912. doi: 10.1002/hbm.24332. Epub 2018 Sep 12. Hum Brain Mapp. 2018. PMID: 30208256 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of first-episode and chronic schizophrenia using multi-modal magnetic resonance imaging.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Oct;22(19):6422-6435. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201810_16055. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30338811
-
Prediction of brain maturity in infants using machine-learning algorithms.Neuroimage. 2016 Aug 1;136:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.05.029. Epub 2016 May 11. Neuroimage. 2016. PMID: 27179605 Free PMC article.
-
Changes of gray matter volume and amplitude of low-frequency oscillations in amnestic MCI: An integrative multi-modal MRI study.Acta Radiol. 2015 May;56(5):614-21. doi: 10.1177/0284185114533329. Epub 2014 May 2. Acta Radiol. 2015. PMID: 24792358
-
Cortical and Subcortical Gray Matter Volume in Youths With Conduct Problems: A Meta-analysis.JAMA Psychiatry. 2016 Jan;73(1):64-72. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2015.2423. JAMA Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26650724 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in functional and diffusion neuroimaging research into the long-term consequences of very preterm birth.J Perinatol. 2021 Apr;41(4):689-706. doi: 10.1038/s41372-020-00865-y. Epub 2020 Oct 24. J Perinatol. 2021. PMID: 33099576 Review.
-
The past, current, and future of neonatal intensive care units with artificial intelligence: a systematic review.NPJ Digit Med. 2023 Nov 27;6(1):220. doi: 10.1038/s41746-023-00941-5. NPJ Digit Med. 2023. PMID: 38012349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Birth weight is associated with adolescent brain development: A multimodal imaging study in monozygotic twins.Hum Brain Mapp. 2020 Dec 15;41(18):5228-5239. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25188. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Hum Brain Mapp. 2020. PMID: 32881198 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of the salience network, ventral attention network, dorsal attention network and default mode network in neonates and early development of the bottom-up attention system.Brain Struct Funct. 2022 Jun;227(5):1843-1856. doi: 10.1007/s00429-022-02477-y. Epub 2022 Mar 14. Brain Struct Funct. 2022. PMID: 35284947
-
Abnormal whole-brain voxelwise structure-function coupling and its association with cognitive dysfunction in patients with different cerebral small vessel disease burdens.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Jun 30;15:1148738. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1148738. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37455935 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Babu, P. , & Stoica, P. (2010). Spectral analysis of nonuniformly sampled data – A review. Digital Signal Processing, 20(2), 359–378. 10.1016/j.dsp.2009.06.019 - DOI
-
- Baldoli, C. , Scola, E. , Della Rosa, P. A. , Pontesilli, S. , Longaretti, R. , Poloniato, A. , … Scifo, P. (2015). Maturation of preterm newborn brains: A fMRI‐DTI study of auditory processing of linguistic stimuli and white matter development. Brain Structure & Function, 220(6), 3733–3751. 10.1007/s00429-014-0887-5 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 602152/PRONIA/International
- KKF 8765162/Kommission für Klinische Forschung, Technische Universität München/International
- BMBF 01ER0803/German Federal Ministry of Education and Science/International
- BMBF 01ER0801/German Federal Ministry of Education and Science/International
- 1336/1-1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

