Concurrent RB1 and TP53 Alterations Define a Subset of EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancers at risk for Histologic Transformation and Inferior Clinical Outcomes
- PMID: 31228622
- PMCID: PMC6764905
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtho.2019.06.002
Concurrent RB1 and TP53 Alterations Define a Subset of EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancers at risk for Histologic Transformation and Inferior Clinical Outcomes
Abstract
Introduction: EGFR-mutant lung cancers are clinically and genomically heterogeneous with concurrent RB transcriptional corepressor 1 (RB1)/tumor protein p53 (TP53) alterations identifying a subset at increased risk for small cell transformation. The genomic alterations that induce lineage plasticity are unknown.
Methods: Patients with EGFR/RB1/TP53-mutant lung cancers, identified by next-generation sequencing from 2014 to 2018, were compared to patients with untreated, metastatic EGFR-mutant lung cancers without both RB1 and TP53 alterations. Time to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor discontinuation, overall survival, SCLC transformation rate, and genomic alterations were evaluated.
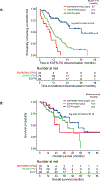
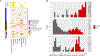
Results: Patients with EGFR/RB1/TP53-mutant lung cancers represented 5% (43 of 863) of EGFR-mutant lung cancers but were uniquely at risk for transformation (7 of 39, 18%), with no transformations in EGFR-mutant lung cancers without baseline TP53 and RB1 alterations. Irrespective of transformation, patients with EGFR/TP53/RB1-mutant lung cancers had a shorter time to discontinuation than EGFR/TP53- and EGFR-mutant -only cancers (9.5 versus 12.3 versus 36.6 months, respectively, p = 2 × 10-9). The triple-mutant population had a higher incidence of whole-genome doubling compared to NSCLC and SCLC at large (80% versus 34%, p < 5 × 10-9 versus 51%, p < 0.002, respectively) and further enrichment in triple-mutant cancers with eventual small cell histology (seven of seven pre-transformed plus four of four baseline SCLC versus 23 of 32 never transformed, respectively, p = 0.05). Activation-induced cytidine deaminase/apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like mutation signature was also enriched in triple-mutant lung cancers that transformed (false discovery rate = 0.03).
Conclusions: EGFR/TP53/RB1-mutant lung cancers are at unique risk of histologic transformation, with 25% presenting with de novo SCLC or eventual small cell transformation. Triple-mutant lung cancers are enriched in whole-genome doubling and Activation-induced cytidine deaminase/apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like hypermutation which may represent early genomic determinants of lineage plasticity.
Keywords: EGFR-mutation; RB1; Small cell histologic transformation; TP53; Whole genome doubling.
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement:
All other authors have declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
Figures

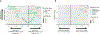
Comment in
-
Histologically Transformed SCLC From EGFR-Mutant NSCLC: Understanding the Wolf in Sheep's Clothing.J Thorac Oncol. 2019 Oct;14(10):1689-1691. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2019.07.010. J Thorac Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31558227 No abstract available.
References
-
- Jordan EJ, Kim HR, Arcila ME, et al. Prospective Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of Lung Adenocarcinomas for Efficient Patient Matching to Approved and Emerging Therapies. Cancer Discov 2017;7:596–609. 10.1158/2159-8290.cd-16-1337. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Piotrowska Z, Isozaki H, Lennerz JK, et al. Landscape of Acquired Resistance to Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC and Clinical Validation of Combined EGFR and RET Inhibition with Osimertinib and BLU-667 for Acquired RET Fusion. Cancer Discov 2018;8:1529–1539. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1022. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

