A hypoallergenic peptide mix containing T cell epitopes of the clinically relevant house dust mite allergens
- PMID: 31228873
- PMCID: PMC7078969
- DOI: 10.1111/all.13956
A hypoallergenic peptide mix containing T cell epitopes of the clinically relevant house dust mite allergens
Abstract
Background: In the house dust mite (HDM) Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus, Der p 1, 2, 5, 7, 21, and 23 have been identified as the most important allergens. The aim of this study was to define hypoallergenic peptides derived from the sequences of the six allergens and to use the peptides and the complete allergens to study antibody, T cell, and cytokine responses in sensitized and nonsensitized subjects.
Methods: IgE reactivity of HDM-allergic and non-HDM-sensitized individuals to 15 HDM allergens was established using ImmunoCAP ISAC technology. Thirty-three peptides covering the sequences of the six HDM allergens were synthesized. Allergens and peptides were tested for IgE and IgG reactivity by ELISA and ImmunoCAP, respectively. Allergenic activity was determined by basophil activation. CD4+ T cell and cytokine responses were determined in PBMC cultures by CFSE dilution and Luminex technology, respectively.
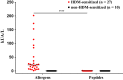
Results: House dust mite allergics showed IgE reactivity only to complete allergens, whereas 31 of the 33 peptides lacked relevant IgE reactivity and allergenic activity. IgG antibodies of HDM-allergic and nonsensitized subjects were directed against peptide epitopes and higher allergen-specific IgG levels were found in HDM allergics. PBMC from HDM-allergics produced higher levels of IL-5 whereas non-HDM-sensitized individuals mounted higher levels of IFN-gamma, IL-17, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and IL-10.
Conclusion: IgG antibodies in HDM-allergic patients recognize peptide epitopes which are different from the epitopes recognized by IgE. This may explain why naturally occurring allergen-specific IgG antibodies do not protect against IgE-mediated allergic inflammation. A mix of hypoallergenic peptides containing T cell epitopes of the most important HDM allergens was identified.
Keywords: T cell epitope; allergen; house dust mite allergy; recombinant allergen; synthetic peptide.
© 2019 The Authors. Allergy Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Valenta reports grants from Biomay AG, Vienna, Austria, grants from Austrian Science Fund, FWF, during the conduct of the study; grants and personal fees from Biomay AG, Vienna, Austria, grants from Austrian Science Fund, FWF, grants and personal fees from Viravaxx, Vienna, Austria, outside the submitted work. Dr. Vrtala reports grants from Austrian Science Fund, during the conduct of the study. All other authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Hypoallergenic Der p 1/Der p 2 combination vaccines for immunotherapy of house dust mite allergy.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012 Aug;130(2):435-43.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.05.035. Epub 2012 Jul 11. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22789398 Free PMC article.
-
IgE Epitopes of the House Dust Mite Allergen Der p 7 Are Mainly Discontinuous and Conformational.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 15;12:687294. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.687294. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34220841 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a Hybrid Vaccine Based on Der f 35-Derived Peptides with Reduced Allergenicity.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2025;186(5):401-417. doi: 10.1159/000541815. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39591953
-
The effect of immunotherapy on cross-reactivity between house dust mite and other allergens in house dust mite -sensitized patients with allergic rhinitis.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2021 Sep;17(9):969-975. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2021.1968834. Epub 2021 Aug 18. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34388949 Review.
-
Hierarchy and molecular properties of house dust mite allergens.Allergol Int. 2015 Oct;64(4):304-11. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2015.05.004. Epub 2015 Jun 13. Allergol Int. 2015. PMID: 26433526 Review.
Cited by
-
The cytoskeletal protein profilin is an important allergen in saltwort (Salsola kali).Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 7;15:1379833. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1379833. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38911871 Free PMC article.
-
Extensively Hydrolyzed Hypoallergenic Infant Formula with Retained T Cell Reactivity.Nutrients. 2022 Dec 26;15(1):111. doi: 10.3390/nu15010111. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36615769 Free PMC article.
-
Preventive Allergen-Specific Vaccination Against Allergy: Mission Possible?Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 7;11:1368. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01368. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32733455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of rAmb a 1-Loaded PLGA-PEG Nanoparticles in a Murine Model of Allergic Conjunctivitis.Molecules. 2022 Jan 18;27(3):598. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030598. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35163859 Free PMC article.
-
Design of an Ara h 2 hypoallergen from conformational epitopes.Clin Exp Allergy. 2024 Jan;54(1):46-55. doi: 10.1111/cea.14433. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Clin Exp Allergy. 2024. PMID: 38168500 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fernandez‐Caldas E, Puerta L, Caraballo L. Mites and allergy. Chem Immunol Allergy. 2014;100:234‐242. - PubMed
-
- Marks GB. House dust mite exposure as a risk factor for asthma: benefits of avoidance. Allergy. 1998;53:108‐114. - PubMed
-
- Thomas WR. IgE and T cell responses to house dust mite allergen components. Mol Immunol. 2018;100:120‐125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

