Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Confers Resistance to BRAF Kinase Inhibitors in Melanoma
- PMID: 31229894
- PMCID: PMC6593146
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2019.06.001
Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Confers Resistance to BRAF Kinase Inhibitors in Melanoma
Abstract
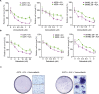
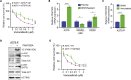
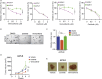
Melanoma frequently harbors oncogenic mutations in the BRAF gene, which drives melanoma growth. Therefore, BRAF kinase inhibitors (BRAFi) are developed and approved for treating BRAF-mutant melanoma. However, the efficacy of BRAFi is limited due to acquired resistance, and in over 40% of melanoma, the causes of BRAFi resistance remain unknown. Here, using a human phospho-receptor tyrosine kinase array we identified Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) as a driver of acquired BRAFi resistance in melanoma. We found that ALK ligand FAM150A was necessary for ALK activation and ALK via the PI3K/AKT pathway was sufficient to confer resistance to BRAFi. ALK inhibitor (ALKi) ceritinib inhibited BRAFi-resistant melanoma in cell culture and mice. Residual BRAFi and ALKi dual resistant melanoma cells from ceritinib-treated mice were sensitive to a broad-spectrum anti-apoptotic protein inhibitor, AT101. Collectively, our results provide a framework for treating BRAF-mutant melanoma that sequentially uses different targeted therapies based on post-treatment tumor evolution.
Keywords: Biological Sciences; Cancer; Cell Biology; Functional Aspects of Cell Biology.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway overcomes the stimulating effect of dabrafenib on the invasive behavior of melanoma cells with acquired resistance to the BRAF inhibitor.Int J Oncol. 2016 Sep;49(3):1164-74. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3594. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27572607
-
Kinase inhibitor library screening identifies synergistic drug combinations effective in sensitive and resistant melanoma cells.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Feb 6;38(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1038-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30728057 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC inhibitors restore BRAF-inhibitor sensitivity by altering PI3K and survival signalling in a subset of melanoma.Int J Cancer. 2018 May 1;142(9):1926-1937. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31199. Epub 2017 Dec 20. Int J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29210065
-
An alternative pathway for cellular protection in BRAF inhibitor resistance in aggressive melanoma type skin cancer.Chem Biol Interact. 2020 May 25;323:109061. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2020.109061. Epub 2020 Mar 17. Chem Biol Interact. 2020. PMID: 32194039 Review.
-
The Role of Senescent Cells in Acquired Drug Resistance and Secondary Cancer in BRAFi-Treated Melanoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 May 7;13(9):2241. doi: 10.3390/cancers13092241. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34066966 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Suppression of heparan sulfation re-sensitizes YAP1-driven melanoma to MAPK pathway inhibitors.Oncogene. 2022 Aug;41(32):3953-3968. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02400-z. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Oncogene. 2022. PMID: 35798875 Free PMC article.
-
Many Distinct Ways Lead to Drug Resistance in BRAF- and NRAS-Mutated Melanomas.Life (Basel). 2021 May 5;11(5):424. doi: 10.3390/life11050424. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34063141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting protein arginine methyltransferase 5 sensitizes glioblastoma to trametinib.Neurooncol Adv. 2022 Jun 20;4(1):vdac095. doi: 10.1093/noajnl/vdac095. eCollection 2022 Jan-Dec. Neurooncol Adv. 2022. PMID: 35875691 Free PMC article.
-
Combating acquired resistance to MAPK inhibitors in melanoma by targeting Abl1/2-mediated reactivation of MEK/ERK/MYC signaling.Nat Commun. 2020 Oct 29;11(1):5463. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19075-3. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33122628 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of cytokine-mediated activation of ALK family receptors.Nature. 2021 Dec;600(7887):143-147. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03959-5. Epub 2021 Oct 13. Nature. 2021. PMID: 34646012 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anastas J.N., Kulikauskas R.M., Tamir T., Rizos H., Long G.V., von Euw E.M., Yang P.T., Chen H.W., Haydu L., Toroni R.A. WNT5A enhances resistance of melanoma cells to targeted BRAF inhibitors. J. Clin. Invest. 2014;124:2877–2890. - PMC - PubMed
- Anastas, J.N., Kulikauskas, R.M., Tamir, T., Rizos, H., Long, G.V., von Euw, E.M., Yang, P.T., Chen, H.W., Haydu, L., Toroni, R.A., et al. (2014). WNT5A enhances resistance of melanoma cells to targeted BRAF inhibitors. J. Clin. Invest. 124, 2877-2890. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Atefi M., von Euw E., Attar N., Ng C., Chu C., Guo D., Nazarian R., Chmielowski B., Glaspy J.A., Comin-Anduix B. Reversing melanoma cross-resistance to BRAF and MEK inhibitors by co-targeting the AKT/mTOR pathway. PLoS One. 2011;6:e28973. - PMC - PubMed
- Atefi, M., von Euw, E., Attar, N., Ng, C., Chu, C., Guo, D., Nazarian, R., Chmielowski, B., Glaspy, J.A., Comin-Anduix, B., et al. (2011). Reversing melanoma cross-resistance to BRAF and MEK inhibitors by co-targeting the AKT/mTOR pathway. PLoS One 6, e28973. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bisserier M., Wajapeyee N. Mechanisms of resistance to EZH2 inhibitors in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood. 2018;131:2125–2137. - PMC - PubMed
- Bisserier, M., and Wajapeyee, N.. (2018). Mechanisms of resistance to EZH2 inhibitors in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood 131, 2125-2137. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bolger M.B., Sherman M.A. Computer modeling of combining site structure of anti-hapten monoclonal antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 1991;203:21–45. - PubMed
- Bolger, M.B., and Sherman, M.A.. (1991). Computer modeling of combining site structure of anti-hapten monoclonal antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 203, 21-45. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

