Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Confers Resistance to BRAF Kinase Inhibitors in Melanoma
- PMID: 31229894
- PMCID: PMC6593146
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2019.06.001
Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Confers Resistance to BRAF Kinase Inhibitors in Melanoma
Abstract
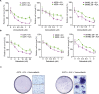
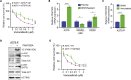
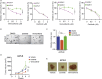
Melanoma frequently harbors oncogenic mutations in the BRAF gene, which drives melanoma growth. Therefore, BRAF kinase inhibitors (BRAFi) are developed and approved for treating BRAF-mutant melanoma. However, the efficacy of BRAFi is limited due to acquired resistance, and in over 40% of melanoma, the causes of BRAFi resistance remain unknown. Here, using a human phospho-receptor tyrosine kinase array we identified Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) as a driver of acquired BRAFi resistance in melanoma. We found that ALK ligand FAM150A was necessary for ALK activation and ALK via the PI3K/AKT pathway was sufficient to confer resistance to BRAFi. ALK inhibitor (ALKi) ceritinib inhibited BRAFi-resistant melanoma in cell culture and mice. Residual BRAFi and ALKi dual resistant melanoma cells from ceritinib-treated mice were sensitive to a broad-spectrum anti-apoptotic protein inhibitor, AT101. Collectively, our results provide a framework for treating BRAF-mutant melanoma that sequentially uses different targeted therapies based on post-treatment tumor evolution.
Keywords: Biological Sciences; Cancer; Cell Biology; Functional Aspects of Cell Biology.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Anastas J.N., Kulikauskas R.M., Tamir T., Rizos H., Long G.V., von Euw E.M., Yang P.T., Chen H.W., Haydu L., Toroni R.A. WNT5A enhances resistance of melanoma cells to targeted BRAF inhibitors. J. Clin. Invest. 2014;124:2877–2890. - PMC - PubMed
- Anastas, J.N., Kulikauskas, R.M., Tamir, T., Rizos, H., Long, G.V., von Euw, E.M., Yang, P.T., Chen, H.W., Haydu, L., Toroni, R.A., et al. (2014). WNT5A enhances resistance of melanoma cells to targeted BRAF inhibitors. J. Clin. Invest. 124, 2877-2890. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Atefi M., von Euw E., Attar N., Ng C., Chu C., Guo D., Nazarian R., Chmielowski B., Glaspy J.A., Comin-Anduix B. Reversing melanoma cross-resistance to BRAF and MEK inhibitors by co-targeting the AKT/mTOR pathway. PLoS One. 2011;6:e28973. - PMC - PubMed
- Atefi, M., von Euw, E., Attar, N., Ng, C., Chu, C., Guo, D., Nazarian, R., Chmielowski, B., Glaspy, J.A., Comin-Anduix, B., et al. (2011). Reversing melanoma cross-resistance to BRAF and MEK inhibitors by co-targeting the AKT/mTOR pathway. PLoS One 6, e28973. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bisserier M., Wajapeyee N. Mechanisms of resistance to EZH2 inhibitors in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood. 2018;131:2125–2137. - PMC - PubMed
- Bisserier, M., and Wajapeyee, N.. (2018). Mechanisms of resistance to EZH2 inhibitors in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood 131, 2125-2137. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bolger M.B., Sherman M.A. Computer modeling of combining site structure of anti-hapten monoclonal antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 1991;203:21–45. - PubMed
- Bolger, M.B., and Sherman, M.A.. (1991). Computer modeling of combining site structure of anti-hapten monoclonal antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 203, 21-45. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

