Achieved oxygen saturations and retinopathy of prematurity in extreme preterms
- PMID: 31229956
- PMCID: PMC6925651
- DOI: 10.1136/archdischild-2018-316464
Achieved oxygen saturations and retinopathy of prematurity in extreme preterms
Abstract
Objective: To identify achieved oxygen saturations (SpO2) associated with increased risk of severe retinopathy of prematurity (ROP).
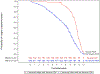
Design: This is a secondary analysis of the Surfactant Positive Airway Pressure and Pulse Oximetry Trial (SUPPORT)randomised controlled trial. SpO2 was recorded up to 36 weeks' postmenstrual age. Saturations through 9 postnatal weeks were explored graphically, and logistic regression models were created to predict severe ROP.
Setting: 20 centres of the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network.
Patients: 984 surviving infants of 24-27 weeks' gestational age born in 2005-2009.
Interventions: SUPPORT targeted SpO2 to a lower (85%-89%) or higher (91%-95%) range through 36 weeks' postmenstrual age or off respiratory support.
Main outcome measures: Severe ROP defined as threshold ROP, ophthalmological surgery or bevacizumab treatment.
Results: There were statistically significant interactions between duration of oxygen supplementation and percentage of time in certain achieved saturation ranges. Specifically, for infants who spent at least 2 weeks on oxygen in postnatal weeks 1-5, a higher percentage of time at 91%-96% SpO2 was associated with increased odds of severe ROP. For infants who spent at least 3 weeks on oxygen in postnatal weeks 6-9, a higher percentage of time at 97%-100% SpO2 was associated with increased odds of severe ROP. Other significant risk factors were lower gestational age and birth weight, non-Hispanic white versus black race, prospectively defined severe illness, late-onset sepsis or meningitis, and clinical centre.
Conclusions: Among extremely preterm survivors to discharge, the association between SpO2 and severe ROP depended on the timing and duration of oxygen supplementation.
Keywords: neonatology; ophthalmology; respiratory.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures



References
-
- Duc G, Sinclair JC. Oxygen administration In: Sinclair JC, Bracken MB, eds. Effective Care of the Newborn Infant. New York: Oxford University Press Inc; 1992. p. 178–94.
-
- Stenson B, Brocklehurst P, Tarnow-Mordi W; U.K. BOOST II trial; Australian BOOST II trial; New Zealand BOOST II trial. Increased 36-week survival with high oxygen saturation target in extremely preterm infants. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(17):1680–2. - PubMed
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Guidelines for perinatal care 6th ed Elk Grove Village (IL): AAP; Washington, DC: ACOG; 2007. p.261–262.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U10 HD021385/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021364/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR008084/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD034216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027871/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025008/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027856/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021373/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD087226/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053124/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053119/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027853/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040521/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053109/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD087229/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003167/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040461/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016587/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040689/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040492/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027853/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027904/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021397/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027904/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025744/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR007122/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027851/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD036790/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040498/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HD095254/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053089/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003142/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024979/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
