Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum probiotics on the serum biochemical parameters, and the vitamin D and leptin receptor genes on mice colon cancer
- PMID: 31231490
- PMCID: PMC6570744
- DOI: 10.22038/ijbms.2019.32624.7806
Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum probiotics on the serum biochemical parameters, and the vitamin D and leptin receptor genes on mice colon cancer
Abstract
Objectives: The preclinical reports have shown that specific probiotics like Bifidobacterium bifidum (B. bifidum) and Lactobacillus acidophilus (L. acidophilus) can be applied as the biotherapeutic agents in the inhibition or therapy of colorectal cancer via the modification of gut bacteria. In the previous studies, we have assessed the impact of L. acidophilus and B. bifidum probiotics on gut bacteria concentration and also their chemo-protective impact on mice colon cancer. In the following, we assessed the effects of these probiotics on the gene expression of vitamin D receptor (VDR) and the leptin receptor (LPR) and the serum biochemical parameters on mice colon cancer.
Materials and methods: Thirty-six male BALB/c mice were equally shared into 4 groups; (i) health with routine dietary foods without any treatment, (ii) azoxymethane (AOM)-induced mice colon cancer with common dietary foods, (iii) and (iv) AOM-induced mice colon cancer with oral consumption of L. acidophilus and B. bifidum (1×109 cfu/g) for 5 months, respectively. Then, the serum total cholesterol, triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL), alanine transaminase, alkaline phosphatase, and albumin and also VDR and LPR genes expression were evaluated.
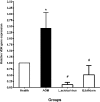
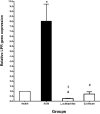
Results: Oral consumption of L. acidophilus and B. bifidum probiotics significantly decreased the triglycerides, alkaline phosphatase, LDL, and also the VDR and LPR gene expression in mice colon cancer (P<0.005).
Conclusion: L. acidophilus and B. bifidum probiotics with the modification of the biochemical parameters and the expression of the VDR and LPR genes can play a key role in the protection of mouse colon cancer.
Keywords: Colon cancer; Leptin receptor; Mice; Probiotic; Vitamin D receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of the manuscript have no conflicts of interest to declare and are responsible for the content of the paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
More Protection of Lactobacillus acidophilus Than Bifidobacterium bifidum Probiotics on Azoxymethane-Induced Mouse Colon Cancer.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2019 Sep;11(3):857-864. doi: 10.1007/s12602-018-9425-8. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2019. PMID: 29682678
-
Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum Probiotics on the Expression of MicroRNAs 135b, 26b, 18a and 155, and Their Involving Genes in Mice Colon Cancer.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2019 Dec;11(4):1155-1162. doi: 10.1007/s12602-018-9478-8. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2019. PMID: 30311185
-
Modifications of mice gut microflora following oral consumption ofLactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum probiotics.Turk J Med Sci. 2017 Apr 18;47(2):689-694. doi: 10.3906/sag-1504-28. Turk J Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28425267
-
Associations of Probiotics with Vitamin D and Leptin Receptors and their Effects on Colon Cancer.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(9):3621-7. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.9.3621. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015. PMID: 25987012 Review.
-
Effects of probiotic bacteria on diarrhea, lipid metabolism, and carcinogenesis: a review of papers published between 1988 and 1998.Am J Clin Nutr. 2000 Feb;71(2):405-11. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/71.2.405. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000. PMID: 10648252 Review.
Cited by
-
Oral probiotics increased the proportion of Treg, Tfr, and Breg cells to inhibit the inflammatory response and impede gestational diabetes mellitus.Mol Med. 2023 Sep 8;29(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s10020-023-00716-4. Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37684563 Free PMC article.
-
Delineating the role of nuclear receptors in colorectal cancer, a focused review.Discov Oncol. 2024 Feb 19;15(1):41. doi: 10.1007/s12672-023-00808-x. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38372868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of L. plantarum KX519413 as Probiotic and Acacia Gum as Prebiotic in Gastrointestinal Tract Strengthening.Microorganisms. 2019 Dec 6;7(12):659. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7120659. Microorganisms. 2019. PMID: 31817751 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotics in Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 12;11:638148. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.638148. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33791223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactobacilli and Bifidobacterium as anti-atherosclerotic agents.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2022 Aug;25(8):934-946. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2022.63860.14073. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 36159325 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kaji R, Kiyoshima-Shibata J, Nagaoka M, Nanno M, Shida K. Bacterial teichoic acids reverse predominant IL-12 production induced by certain lactobacillus strains into predominant IL-10 production via TLR2-dependent ERK activation in macrophages. J Immunol. 2010;184:3505–3513. - PubMed
-
- Ranji P, Akbarzadeh A, Rahmati-Yamchi M. Associations of probiotics with vitamin D and leptin receptors and their effects on colon cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16:3621–3627. - PubMed
-
- Khavari-Daneshvar H, Mosavi M, Khodayari H, Rahimi E, Ranji P, Mohseni AH, et al. Modifications of mice gut microflora following oral consumption of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum probiotics. Turk J Med Sci. 2017;47:689–694. - PubMed
-
- Agah S, Alizadeh AM, Mosavi M, Ranji P, Khavari-Daneshvar H, Ghasemian F, et al. More Protection of Lactobacillus acidophilus than Bifidobacterium bifidum probiotics on azoxymethane-induced mouse colon cancer. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2018;10:1. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources