Effect on osseointegration of two implant macro-designs:A histomorphometric analysis of bicortically installed implants in different topographic sites of rabbit's tibiae
- PMID: 31232382
- PMCID: PMC6667005
- DOI: 10.4317/medoral.22825
Effect on osseointegration of two implant macro-designs:A histomorphometric analysis of bicortically installed implants in different topographic sites of rabbit's tibiae
Abstract
Background: To evaluate the effect of two different implant macro-designs on the sequential osseointegration at bicortically installed implants in the rabbit tibia. A further aim is to compare the osseointegration at different topographic zones.
Material and methods: 27 New Zealand rabbits were implemented. Two implants, one for each macro-design (Ticare Inhex® or Ticare Quattro®, Mozo-Grau, Valladolid, Spain), were randomly implanted in the diaphysis or metaphysis of each tibia. The flaps were sutured to allow a submerged healing. The animals were sacrificed after 2, 4 or 8 weeks. Ground sections were prepared and analyzed.
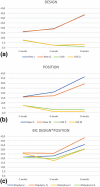
Results: No statistically significant differences were found between the two groups for newly formed bone in contact with the implant surface, being about 16%, 19% and 33% in both groups, after 2, 4, and 8 weeks of healing. Bone apposition was slightly higher in the diaphysis, reaching values of 36.4% in the diaphysis, and 29.3% in the metaphysis at 8 weeks of healing. It was observed that the implant position showed a statistical significance regarding BIC values at 4 and 8 weeks (p<0.05). Multivariate analysis fails to detect statistical significant differences for the interaction between implant designs and topographic site. Ticare Quattro® design had a slight better BIC values at diaphysis sites across healing stages, but without reaching a statistical significance.
Conclusions: The both implant macro-designs provided similar degrees of osseointegration. Bone morphometry and density may affect bone apposition onto the implant surface. The apposition rates were slightly better in diaphysis compared to metaphysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bone-Healing Pattern on the Surface of Titanium Implants at Cortical and Marrow Compartments in Two Topographic Sites: an Experimental Study in Rabbits.Materials (Basel). 2018 Dec 27;12(1):85. doi: 10.3390/ma12010085. Materials (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30591652 Free PMC article.
-
Bone healing at bicortically installed implants with different surface configurations. An experimental study in rabbits.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015 Mar;26(3):293-9. doi: 10.1111/clr.12475. Epub 2014 Sep 15. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015. PMID: 25220835
-
Bone healing at collagenated bicortically installed implants: an experimental study in rabbits.Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020 Dec;24(4):501-507. doi: 10.1007/s10006-020-00882-3. Epub 2020 Jul 11. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020. PMID: 32653997
-
Effect of insertion torque on titanium implant osseointegration: an animal experimental study.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015 Feb;26(2):191-6. doi: 10.1111/clr.12316. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015. PMID: 24325598
-
Effects on the osseointegration of titanium implants incorporating calcium-magnesium: a resonance frequency and histomorphometric analysis in rabbit tibia.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018 Jul;29(7):785-791. doi: 10.1111/clr.12909. Epub 2016 Jul 6. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018. PMID: 27381553
Cited by
-
Impact of lattice versus solid structure of 3D-printed multiroot dental implants using Ti-6Al-4V: a preclinical pilot study.J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2022 Aug;52(4):338-350. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2105720286. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36047586 Free PMC article.
-
mRNA encoding bone morphogenetic protein-2 facilitated peri-implant bone formation of titanium implants placed in rat femurs.Sci Rep. 2025 May 22;15(1):17852. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02931-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40404873 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of thin-threaded implants primary stability in type IV bone right after maxillary sinus floor elevation: A human cadaver study.J Prosthodont. 2025 Jul;34(6):593-601. doi: 10.1111/jopr.13983. Epub 2024 Nov 14. J Prosthodont. 2025. PMID: 39539131 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between dental implant macro-design and osseointegration: a systematic review.Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2024 Mar;28(1):1-14. doi: 10.1007/s10006-022-01116-4. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2024. PMID: 36171302
-
Coating Ti6Al4V implants with nanocrystalline diamond functionalized with BMP-7 promotes extracellular matrix mineralization in vitro and faster osseointegration in vivo.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 28;12(1):5264. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09183-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35347219 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schroeder A, Pohler O, Sutter F. [Tissue reaction to an implant of a titanium hollow cylinder with a titanium surface spray layer] Schweizerische Monatsschrift fur Zahnheilkd. 1976;86:713–27. - PubMed
-
- Albrektsson T, Eriksson AR, Friberg B, Lekholm U, Lindahl L, Nevins M. Histologic investigations on 33 retrieved Nobelpharma implants. Clin Mater. 1993;12:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Botticelli D, Lang NP. Dynamics of osseointegration in various human and animal models - a comparative analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2017;28:742–8. - PubMed
-
- Lioubavina-Hack N, Lang NP, Karring T. Significance of primary stability for osseointegration of dental implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006;17:244–50. - PubMed
-
- Marco F, Milena F, Gianluca G, Vittoria O. Peri-implant osteogenesis in health and osteoporosis. Micron. 2005;36:630–44. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

