Control of Anticoagulation Therapy in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Treated with Warfarin: A Study from the Chinese Atrial Fibrillation Registry
- PMID: 31232394
- PMCID: PMC6604671
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.917131
Control of Anticoagulation Therapy in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Treated with Warfarin: A Study from the Chinese Atrial Fibrillation Registry
Abstract
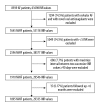
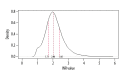
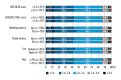
BACKGROUND Several factors determine the efficacy of warfarin anticoagulation in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF). This study aimed to use data from the Chinese Atrial Fibrillation Registry study to assess the control of anticoagulation therapy in Chinese patients with NVAF treated with warfarin. MATERIAL AND METHODS From the Chinese Atrial Fibrillation Registry study the anticoagulant use and dosing, the time in therapeutic range (TTR) of the international normalized ratio (INR), and standard deviation of the observed INR values (SDINR), and their influencing factors were evaluated. RESULTS The median INR and SDINR were 2.04 (IQR 1.71-2.41) and 0.50 (IQR, 0.35-0.69), respectively. The median TTR was 51.7% (IQR, 30.6-70.1%) and only 25.1% had a TTR ≥70%. Age was ≥70 years (OR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.55-0.94; P=0.015), bleeding history (OR 0.48; 95% CI, 0.23-0.89; P=0.029), the use of a single drug (OR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.42-0.92; P=0.016), more than drug (OR, 0.60; 95% CI, 0.41-0.88; P=0.009), and lack of assessment of bleeding risk (OR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.54-0.97; P=0.033) were associated with TTR <70% (INR 2.0-3.0). Coronary heart disease (CHD) and peripheral artery disease (PAD) (OR, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.52-0.90; P=0.007) and diabetes mellitus (OR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.62-0.99; P=0.044) were associated with increased variability in INR (SDINR ≥0.5). CONCLUSIONS In Chinese patients with NVAF, warfarin anticoagulation was associated with lower TTR and less stable anticoagulation than in current guidelines, and risk factors for reduced safety and efficacy were identified.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Chang-Sheng Ma has received honoraria from Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS), Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, Boehringer Ingelheim (BI), and Bayer for giving lectures. Dr. Jian-Zeng Dong also received honoraria from Johnson & Johnson for giving lectures. Dr. Gregory Y.H. Lip is a Consultant for Bayer/Janssen, BMS/Pfizer, Medtronic, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Verseon, and Daiichi-Sankyo, and is a speaker for Bayer, BMS/Pfizer, Medtronic, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Daiichi-Sankyo. No fees were directly received personally regarding this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Warfarin Management and Outcomes in Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation Within an Integrated Health Care System.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2017 Jun;23(6):700-712. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2017.23.6.700. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2017. PMID: 28530526 Free PMC article.
-
Anticoagulation Control, Outcomes, and Associated Factors in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Receiving Warfarin at Tertiary Care Hospital in Ethiopia.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2021 Jan-Dec;27:10760296211049786. doi: 10.1177/10760296211049786. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2021. PMID: 34724849 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the impact of warfarin time in therapeutic range on outcomes of patients with atrial fibrillation in Turkey: perspectives from the observational, prospective WATER Registry.Cardiol J. 2015;22(5):567-75. doi: 10.5603/CJ.a2015.0035. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Cardiol J. 2015. PMID: 26100825
-
Meta-Analysis Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Low-Intensity Warfarin for Patients >65 Years of Age With Non-Valvular Atrial Fibrillation.Am J Cardiol. 2021 Mar 1;142:74-82. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2020.12.001. Epub 2020 Dec 8. Am J Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33307015 Review.
-
Meta-Analysis of Safety and Efficacy of Direct Oral Anticoagulants Versus Warfarin According to Time in Therapeutic Range in Atrial Fibrillation.Am J Cardiol. 2021 Feb 1;140:62-68. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2020.10.064. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Am J Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33189659
Cited by
-
Efficacy and Safety of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Stable Coronary Artery Disease and Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2022 Jan-Dec;28:10760296221131033. doi: 10.1177/10760296221131033. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2022. PMID: 36198012 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship of adverse events to quality of anticoagulation control in atrial fibrillation patients with diabetes: real-world data from the FANTASIIA Registry.Ann Med. 2020 Sep;52(6):300-309. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2020.1778176. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Ann Med. 2020. PMID: 32500748 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and Safety of the Coadministration of Rifampin and Warfarin versus Direct Oral Anticoagulants: A Cohort Study.Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2024 Sep 25;2024:9694592. doi: 10.1155/2024/9694592. eCollection 2024. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 39359455 Free PMC article.
-
The Characteristics, Long-Term Outcomes, Risk Factors, and Antithrombotic Therapy in Chinese Patients With Atrial Fibrillation and Bioprosthetic Valves.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Jun 10;8:665124. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.665124. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34179131 Free PMC article.
-
Social App to Improve Warfarin Therapy in Post-MHVR Chinese Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Cardiovasc Ther. 2023 Jan 14;2023:2342111. doi: 10.1155/2023/2342111. eCollection 2023. Cardiovasc Ther. 2023. PMID: 36714197 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Lip G, Freedman B, De Caterina R, Potpara TS. Stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation: Past, present and future. Comparing the guidelines and practical decision-making. Thromb Haemost. 2017;117(7):1230–39. - PubMed
-
- Shen AY, Yao JF, Brar SS, et al. Racial/ethnic differences in the risk of intracranial haemorrhage among patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;50(4):309–15. - PubMed
-
- Huang CX, Zhang S, Huang DJ, et al. Current knowledge and management recommendations of atrial fibrillation 2015. Chin J Cardiac Arrhyth. 2015;5:321–84.
-
- Ogawa S, Koretsune Y, Yasaka M, et al. Antithrombotic therapy in atrial fibrillation: Evaluation and positioning of new oral anticoagulant agents. Circ J. 2011;75(7):1539–47. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

