Inhibition of inflammation by minocycline improves heart failure and depression-like behaviour in rats after myocardial infarction
- PMID: 31233508
- PMCID: PMC6590948
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217437
Inhibition of inflammation by minocycline improves heart failure and depression-like behaviour in rats after myocardial infarction
Abstract
Rationale: Patients with heart failure have an increased incidence of depression. Central and peripheral inflammation play a major role in the pathophysiology of both heart failure and depression.
Aim: Minocycline is an antibiotic that inhibits microglia activation and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. We assessed effects of minocycline on extent of heart failure and depression at 2 and 8 weeks post myocardial infarction.
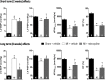
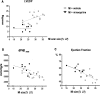
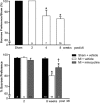
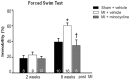
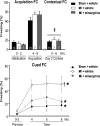
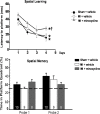
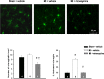
Methods/results: Male Wistar rats were randomly divided into 3 groups: (i) sham + vehicle; (ii) MI + vehicle; and (iii) MI + minocycline with n/group of 8, 9 and 9 at 2 weeks, and 10, 16, 8 at weeks, respectively. Oral minocycline (50 mg/kg/day) or vehicle started 2 days before surgery. Depression-like behaviour was assessed with sucrose preference and forced swim tests, and cardiac function with echo and hemodynamics. After myocardial infarction, microglia activation and plasma/brain pro-inflammatory cytokines increased, which were mostly prevented by minocycline. At 8 weeks, cardiac dysfunction was attenuated by minocycline: infarct size (MI + Vehicle 29±1, MI + Min 23±1%), ejection fraction (Sham 80±1, MI + Vehicle 48±2, MI + Min 58±2%) and end diastolic pressure (Sham 3.2±0.3, MI + Vehicle 18.2±1.1, MI + Min 8.5±0.9 mm Hg). Depression-like behaviour was significantly improved by minocycline in sucrose preference test (% Sucrose Intake: Sham 96±1, MI + Vehicle 78±2, MI + Min 87±2) and forced swim test (% Immobile: Sham 40±4, MI + Vehicle 61±3, MI + Min 37±6).
Conclusion: Rats post myocardial infarction develop systemic inflammation, heart failure and depression-like behaviour that are all attenuated by minocycline. Targeting (neuro) inflammation may represent new therapeutic strategy for patients with heart failure and depression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of Myocardial Infarction-Induced Neuroinflammation for Depression-Like Behavior and Heart Failure in Ovariectomized Female Rats.Neuroscience. 2019 Sep 1;415:201-214. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.07.017. Epub 2019 Jul 24. Neuroscience. 2019. PMID: 31351141
-
Improvement of renal dysfunction in rats with chronic heart failure after myocardial infarction by treatment with the endothelin A receptor antagonist, LU 135252.J Hypertens. 2000 Oct;18(10):1507-14. doi: 10.1097/00004872-200018100-00020. J Hypertens. 2000. PMID: 11057440
-
Sex differences in depression-like behavior and neuroinflammation in rats post-MI: role of estrogens.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018 Nov 1;315(5):H1159-H1173. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00615.2017. Epub 2018 Jul 27. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30052050 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical aspects of left ventricular diastolic function assessed by Doppler echocardiography following acute myocardial infarction.Dan Med Bull. 2001 Nov;48(4):199-210. Dan Med Bull. 2001. PMID: 11767125 Review.
-
Immunomodulatory interventions in myocardial infarction and heart failure: a systematic review of clinical trials and meta-analysis of IL-1 inhibition.Cardiovasc Res. 2018 Sep 1;114(11):1445-1461. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvy145. Cardiovasc Res. 2018. PMID: 30010800 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Death-Associated Protein Kinase 1 (DAPK1) Protects against Myocardial Injury Induced by Myocardial Infarction in Rats via Inhibition of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress.Dis Markers. 2022 Jan 17;2022:9651092. doi: 10.1155/2022/9651092. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35082934 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Neuroinflammation and Cognitive Decline in Patients with Cardiac Disease: Evidence, Relevance, and Therapeutic Implications.Life (Basel). 2023 Jan 24;13(2):329. doi: 10.3390/life13020329. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shuangxinfang Prevents S100A9-Induced Macrophage/Microglial Inflammation to Improve Cardiac Function and Depression-Like Behavior in Rats After Acute Myocardial Infarction.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 24;13:832590. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.832590. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35814253 Free PMC article.
-
Minocycline as heart conditioning agent in experimental type 2 diabetes mellitus - an antibacterial drug in heart protection.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022 Apr;395(4):429-444. doi: 10.1007/s00210-021-02179-y. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35113200
-
Mechanism and therapeutic strategies of depression after myocardial infarction.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021 Jun;238(6):1401-1415. doi: 10.1007/s00213-021-05784-0. Epub 2021 Feb 16. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021. PMID: 33594503 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

