Sustainable Green Pavement Using Bio-Based Polyurethane Binder in Tunnel
- PMID: 31234287
- PMCID: PMC6630764
- DOI: 10.3390/ma12121990
Sustainable Green Pavement Using Bio-Based Polyurethane Binder in Tunnel
Abstract
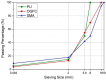
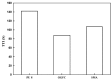
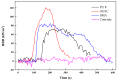
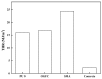
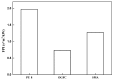
As a closed space, the functional requirements of the tunnel pavement are very different from ordinary pavements. In recent years, with the increase of requirements for tunnel pavement safety, comfort and environmental friendliness, asphalt pavement has become more and more widely used in long tunnels, due to its low noise, low dust, easy maintenance, and good comfort. However, conventional tunnel asphalt pavements cause significant safety and environmental concerns. The innovative polyurethane thin overlay (PTO) has been developed for the maintenance of existing roads and constructing new roads. Based on the previous study, the concept of PTO may be a feasible and effective way to enrich the innovative functions of tunnel pavement. In this paper, the research aims to evaluate the functional properties of PTO, such as noise reduction, solar reflection and especially combustion properties. Conventional asphalt (Open-graded Friction Course (OGFC) and Stone Mastic Asphalt (SMA)) and concrete pavement materials were used as control materials. Compared with conventional tunnel pavement materials, significant improvements were observed in functional properties and environmental performance. Therefore, this innovative wearing layer can potentially provide pavements with new eco-friendly functions. This study provides a comprehensive analysis of these environmentally friendly materials, paving the way for the possible application in tunnels, as well as some other fields, such as race tracks in stadiums.
Keywords: combustion properties; noise reduction; polyurethane thin overlay; solar reflection; sustainable pavement material; tunnel pavement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Zhang J., Wang M., Wang D., Li X., Song B., Liu P. Feasibility study on measurement of a physiological index value with an electrocardiogram tester to evaluate the pavement evenness and driving comfort. Measurement. 2018;117:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2017.11.060. - DOI
-
- Liu P., Otto F., Wang D., Oeser M., Balck H. Measurement and evaluation on deterioration of asphalt pavements by geophones. Measurement. 2017;109:223–232. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2017.05.066. - DOI
-
- Jolitz R.J., Kirk D.R. Flame Retardant Asphalt Composition. 4,804,696. U.S. Patent. 1989 Feb 14;
-
- Walters R.B. Flame Retarded Asphalt Blend Composition. 4,659,381. U.S. Patent. 1987 Apr 21;
-
- Grube L.L., Frankoski S.P. Flame Retardant Bitumen. 5,110,674. U.S. Patent. 1992 May 5;
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

