IQSEC2-Associated Intellectual Disability and Autism
- PMID: 31234416
- PMCID: PMC6628259
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20123038
IQSEC2-Associated Intellectual Disability and Autism
Abstract
Mutations in IQSEC2 cause intellectual disability (ID), which is often accompanied by seizures and autism. A number of studies have shown that IQSEC2 is an abundant protein in excitatory synapses and plays an important role in neuronal development as well as synaptic plasticity. Here, we review neuronal IQSEC2 signaling with emphasis on those aspects likely to be involved in autism. IQSEC2 is normally bound to N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-type glutamate receptors via post synaptic density protein 95 (PSD-95). Activation of NMDA receptors results in calcium ion influx and binding to calmodulin present on the IQSEC2 IQ domain. Calcium/calmodulin induces a conformational change in IQSEC2 leading to activation of the SEC7 catalytic domain. GTP is exchanged for GDP on ADP ribosylation factor 6 (ARF6). Activated ARF6 promotes downregulation of surface α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA)-type glutamate receptors through a c-jun N terminal kinase (JNK)-mediated pathway. NMDA receptors, AMPA receptors, and PSD-95 are all known to be adversely affected in autism. An IQSEC2 transgenic mouse carrying a constitutively active mutation (A350V) shows autistic features and reduced levels of surface AMPA receptor subunit GluA2. Sec7 activity and AMPA receptor recycling are presented as two targets, which may respond to drug treatment in IQSEC2-associated ID and autism.
Keywords: AMPA receptors; NMDA receptors; autism; guanine nucleotide exchange factor; intellectual disability; synaptic plasticity.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
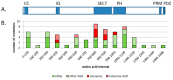
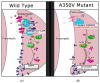
References
-
- Shoubridge C., Tarpey P.S., Abidi F., Ramsden S.L., Rujirabanjerd S., Murphy J.S., Boyle J., Shaw M., Gardner A., Proos A., et al. Mutations in the guanine nucleotide exchange factor gene IQSEC2 cause non-syndromic intellectual disability. Nat. Genet. 2010;42:486–488. doi: 10.1038/ng.588. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mignot C., McMahon A.C., Bar C., Campeau P.M., Davidson C., Buratti J., Nava C., Jacquemont M.L., Tallot M., Milh M., et al. IQSEC2-related encephalopathy in males and females: a comparative study including 37 novel patients. Genet. Med. 2019;4:837–849. doi: 10.1038/s41436-018-0268-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sakagami H., Sanda M., Fukaya M., Miyazaki T., Sukegawa J., Yanagisawa T., Suzuki T., Fukunaga K., Watanabe M., Kondo H. IQ-ArfGEF/BRAG1 is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Arf6 that interacts with PSD-95 at postsynaptic density of excitatory synapses. Neurosci. Res. 2008;60:199–212. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2007.10.013. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

