Bioactive Peptide VHVV Upregulates the Long-Term Memory-Related Biomarkers in Adult Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
- PMID: 31234585
- PMCID: PMC6627188
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20123069
Bioactive Peptide VHVV Upregulates the Long-Term Memory-Related Biomarkers in Adult Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
Abstract
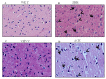
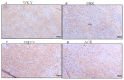
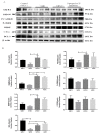
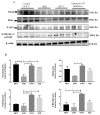
Hypertension is one of the growing risk factors for the progression of long-term memory loss. Hypertension-mediated memory loss and treatment remain not thoroughly elucidated to date. Plant-based natural compounds are an alternative solution to treating human diseases without side effects associated with commercial drugs. This study reveals that bioactive peptides extracted from soy hydrolysates mimic hypertension-mediated memory loss and neuronal degeneration and alters the memory molecular pathway in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). The SHR animal model was treated with bioactive peptide VHVV (10 mg/kg/oral administration) and angiotensin-converting-enzyme (ACE) inhibitors (5 mg/kg/oral administration) for 24 weeks. We evaluated molecular level expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), cAMP response element binding protein (CREB), and survival markers phospho-protein kinase B (P-AKT) and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) after 24 weeks of treatment for SHR in this study. Western blotting, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, and immunohistochemistry showed long-term memory loss and neuronal degeneration in SHR animals. Bioactive peptide VHVV-treated animals upregulated the expression of long-term memory-relate proteins and neuronal survival. Spontaneously hypertensive rats treated with oral administration of bioactive peptide VHVV had activated CREB-mediated downstream proteins which may reduce hypertension-mediated long-term memory loss and maintain neuronal survival.
Keywords: angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor; bioactive peptide; blood–brain barrier; long-term memory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
VH-4-A Bioactive Peptide from Soybean and Exercise Training Constrict Hypertension in Rats through Activating Cell Survival and AMPKα1, Sirt1, PGC1α, and FoX3α.Molecules. 2022 Nov 9;27(22):7705. doi: 10.3390/molecules27227705. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36431802 Free PMC article.
-
Dipeptide IF prevents the effects of hypertension-induced Alzheimer's disease on long-term memory in the cortex of spontaneously hypertensive rats.Environ Toxicol. 2020 May;35(5):570-581. doi: 10.1002/tox.22892. Epub 2019 Dec 30. Environ Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 31889399
-
Aluminium chloride impairs long-term memory and downregulates cAMP-PKA-CREB signalling in rats.Toxicology. 2014 Sep 2;323:95-108. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2014.06.011. Epub 2014 Jun 25. Toxicology. 2014. PMID: 24973631
-
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers Attenuate Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Memory Impairment by Modulation of NF-κB-Mediated BDNF/CREB Expression and Apoptosis in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Feb;55(2):1725-1739. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0450-5. Epub 2017 Feb 18. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28215000
-
Effect of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from rice dregs protein on antihypertensive activity in spontaneously hypertensive rats.Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2007;16 Suppl 1:281-5. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2007. PMID: 17392119
Cited by
-
Preparation, Characterization, and Cytoprotective Effects on HUVECs of Fourteen Novel Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides From Protein Hydrolysate of Tuna Processing By-Products.Front Nutr. 2022 Apr 14;9:868681. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.868681. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35495901 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Novel ACE-Inhibitory Peptides from Nemopilema nomurai Jellyfish Venom Hydrolysate: In Vitro and In Silico Approaches.Mar Drugs. 2025 Jun 26;23(7):267. doi: 10.3390/md23070267. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40710492 Free PMC article.
-
VH-4-A Bioactive Peptide from Soybean and Exercise Training Constrict Hypertension in Rats through Activating Cell Survival and AMPKα1, Sirt1, PGC1α, and FoX3α.Molecules. 2022 Nov 9;27(22):7705. doi: 10.3390/molecules27227705. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36431802 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in exploring and exploiting soybean functional peptides-a review.Front Nutr. 2023 Jun 15;10:1185047. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1185047. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37396130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alterations in cellular metabolisms after TKI therapy for Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemia in children: A review.Front Oncol. 2022 Dec 6;12:1072806. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1072806. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36561525 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Obisesan T.O., Obisesan O.A., Martins S., Alamgir L., Bond V., Maxwell C., Gillum R.F. High blood pressure, hypertension, and high pulse pressure are associated with poorer cognitive function in persons aged 60 and older: The Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2008 doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2007.01592.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shih Y.H., Tsai S.F., Huang S.H., Chiang Y.T., Hughes M.W., Wu S.Y., Lee C.W., Yang T.T., Kuo Y.M. Hypertension impairs hippocampus-related adult neurogenesis, CA1 neuron dendritic arborization and long-term memory. Neuroscience. 2016;322:346–357. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.02.045. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jivad N., Rabiei Z. A review study on medicinal plants used in the treatment of learning and memory impairments. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2014;4:780–789. doi: 10.12980/APJTB.4.2014APJTB-2014-0412. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

