A Gene Regulatory Network Controlled by BpERF2 and BpMYB102 in Birch under Drought Conditions
- PMID: 31234595
- PMCID: PMC6627136
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20123071
A Gene Regulatory Network Controlled by BpERF2 and BpMYB102 in Birch under Drought Conditions
Abstract
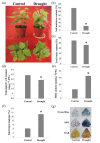
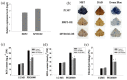
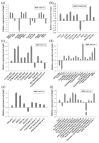
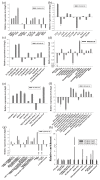
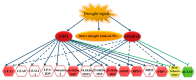
Gene expression profiles are powerful tools for investigating mechanisms of plant stress tolerance. Betula platyphylla (birch) is a widely distributed tree, but its drought-tolerance mechanism has been little studied. Using RNA-Seq, we identified 2917 birch genes involved in its response to drought stress. These drought-responsive genes include the late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) family, heat shock protein (HSP) family, water shortage-related and ROS-scavenging proteins, and many transcription factors (TFs). Among the drought-induced TFs, the ethylene responsive factor (ERF) and myeloblastosis oncogene (MYB) families were the most abundant. BpERF2 and BpMYB102, which were strongly induced by drought and had high transcription levels, were selected to study their regulatory networks. BpERF2 and BpMYB102 both played roles in enhancing drought tolerance in birch. Chromatin immunoprecipitation combined with qRT-PCR indicated that BpERF2 regulated genes such as those in the LEA and HSP families, while BpMYB102 regulated genes such as Pathogenesis-related Protein 1 (PRP1) and 4-Coumarate:Coenzyme A Ligase 10 (4CL10). Multiple genes were regulated by both BpERF2 and BpMYB102. We further characterized the function of some of these genes, and the genes that encode Root Primordium Defective 1 (RPD1), PRP1, 4CL10, LEA1, SOD5, and HSPs were found to be involved in drought tolerance. Therefore, our results suggest that BpERF2 and BpMYB102 serve as transcription factors that regulate a series of drought-tolerance genes in B. platyphylla to improve drought tolerance.
Keywords: Betula platyphylla; RNA-Seq; drought stress; expression regulatory network; transcription factor; transient transformation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification of R2R3-MYB transcription factors in Betula platyphylla and functional analysis of BpMYB95 in salt tolerance.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Nov;279(Pt 2):135193. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135193. Epub 2024 Aug 30. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39216584
-
Expression analysis of the BpARF genes in Betula platyphylla under drought stress.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2020 Mar;148:273-281. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.01.028. Epub 2020 Jan 21. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2020. PMID: 31986481
-
The BpPP2C-BpMADS11-BpERF61 signaling confers drought tolerance in Betula platyphylla.New Phytol. 2024 Dec;244(6):2364-2381. doi: 10.1111/nph.20164. Epub 2024 Oct 1. New Phytol. 2024. PMID: 39351656
-
The potential of transcription factor-based genetic engineering in improving crop tolerance to drought.OMICS. 2014 Oct;18(10):601-14. doi: 10.1089/omi.2013.0177. Epub 2014 Aug 13. OMICS. 2014. PMID: 25118806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant tolerance to drought and salinity: stress regulating transcription factors and their functional significance in the cellular transcriptional network.Plant Cell Rep. 2011 Aug;30(8):1383-91. doi: 10.1007/s00299-011-1068-0. Epub 2011 Apr 8. Plant Cell Rep. 2011. PMID: 21476089 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and characterization of 5 walnut MYB genes in response to drought stress involved in ABA signaling.Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2021 Jun;27(6):1323-1335. doi: 10.1007/s12298-021-01008-z. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2021. PMID: 34177150 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles on Gene Expression of Birch Clones In Vitro under Stress Caused by Phytopathogens.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Mar 4;12(5):864. doi: 10.3390/nano12050864. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35269352 Free PMC article.
-
NADPH Oxidase RbohD and Ethylene Signaling are Involved in Modulating Seedling Growth and Survival Under Submergence Stress.Plants (Basel). 2020 Apr 8;9(4):471. doi: 10.3390/plants9040471. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32276372 Free PMC article.
-
The Artificial Promoter rMdAG2I Confers Flower-specific Activity in Malus.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 13;20(18):4551. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184551. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31540316 Free PMC article.
-
An efficient screening system of disease-resistant genes from wild apple, Malus sieversii in response to Valsa mali pathogenic fungus.Plant Methods. 2023 Dec 2;19(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s13007-023-01115-w. Plant Methods. 2023. PMID: 38042829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mutwakil M.Z., Hajrah N.H., Atef A., Edris S., Sabir M.J., Al-Ghamdi A.K., Sabir M.J.S.M., Nelson C., Makki R.M., Ali H.M., et al. Transcriptomic and metabolic responses of Calotropis procera to salt and drought stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2017;17:231. doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-1155-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

