A meta-analysis of MDR1 polymorphisms rs1128503 and rs1045642 and susceptibility to hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 31234681
- PMCID: PMC6683882
- DOI: 10.1177/0300060519855869
A meta-analysis of MDR1 polymorphisms rs1128503 and rs1045642 and susceptibility to hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Objective: A relationship between polymorphisms rs1128503 and rs1045642 in the multidrug resistance 1 gene (MDR1) and susceptibility to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has been reported but is inconclusive. This study was performed to explore the significance of MDR1 polymorphisms rs1128503 and rs1045642 in screening and diagnosis of HCC.
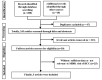
Methods: Studies of association analyses between MDR1 gene polymorphisms rs1128503 and rs1045642 and HCC were selected from three foreign language databases (PubMed, Cochrane, and Embase) and three Chinese databases (Wanfang, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, and China Knowledge Network) and subjected to meta-analysis.
Results: We found no significant relationship between the rs1128503 polymorphism and susceptibility to HCC in 4 cohorts and no significant relationship between the rs1045642 polymorphism and susceptibility to HCC in 3 cohorts.
Conclusions: There was no relationship between polymorphisms rs1128503 or rs1045642 of the MDR1 gene and susceptibility to HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); P-glycoprotein; meta-analysis; multidrug resistance 1 (MDR1); polymorphism; susceptibility.
Figures



References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2015; 65: 87–108. - PubMed
-
- Mann JF, Schmieder RE, McQueen M, et al. Renal outcomes with telmisartan, ramipril, or both, in people at high vascular risk (the ONTARGET study): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, controlled trial. Lancet 2008; 372: 547–553. - PubMed
-
- Jamroziak K, Mlynarski W, Balcerczak E, et al. Functional C3435T polymorphism of MDR1 gene: an impact on genetic susceptibility and clinical outcome of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Eur J Haematol 2004; 72: 314–321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

