microRNA-98 protects sepsis mice from cardiac dysfunction, liver and lung injury by negatively regulating HMGA2 through inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway
- PMID: 31234706
- PMCID: PMC6681783
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1635869
microRNA-98 protects sepsis mice from cardiac dysfunction, liver and lung injury by negatively regulating HMGA2 through inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway
Retraction in
-
Statement of Retraction: microRNA-98 protects sepsis mice from cardiac dysfunction, liver and lung injury by negatively regulating HMGA2 through inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway.Cell Cycle. 2022 Dec;21(23):2552. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2097800. Epub 2022 Jul 15. Cell Cycle. 2022. PMID: 35838559 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
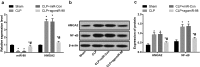
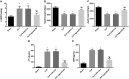
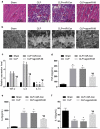
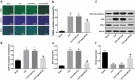
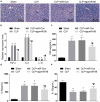
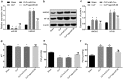
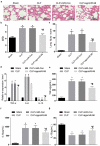
Recently, MicroRNA-98 (miR-98) works as a biomarker in some diseases, such as lung cancer, Schizophrenia, and breast cancer, but there still lack of studies on the function of miR-98 during sepsis. Thus, our study is conducted to figure out the function of miR-98 for the regulation of cardiac dysfunction, liver and lung injury in sepsis mice. Cecum ligation and puncture was used to establish the sepsis mice model. Next, miR-Con and agomiR-98 were injected into the tail vein of mice 48 h after modeling. Then, expression of miR-98, HMGA2, NF-κB, inflammatory factors, apoptosis-related proteins in myocardial, liver and lung tissues of septic mice were determined. Moreover, other indices that were associated with cardiac dysfunction, liver and lung injury in septic mice were detected. Finally, bioinformatics analysis and luciferase activity assay were utilized to validate the binding site between miR-98 and HMGA2. miR-98 was poorly expressed, while HMGA2, NF-κB pathway-related proteins were highly expressed in myocardial, liver, and lung tissues of mice with sepsis. Upregulated miR-98 inhibited HMGA2, NF-κB, TNF-α, IL-6, Bcl-2 and increased IL-10, Cleaved caspase-3 and Bax expression in myocardial, liver, and lung tissues of septic mice. Upregulation of miR-98 decreased LVEDP, CTn-I, BNP, ALT, AST, TBIL, LDH, and PaCO2 while increased +dp/dt max, -dp/dt max, pH and PaO2 in sepsis mice. miR-98 was a direct target gene of HMGA2. Our study provides evidence that miR-98 protects sepsis mice from cardiac dysfunction, liver and lung injury by negatively mediating HMGA2 via the inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway.
Keywords: HMGA2; MicroRNA-98; sepsis.
Figures

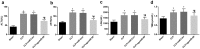
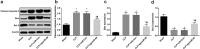
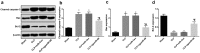

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-150 affects endoplasmic reticulum stress via MALAT1-miR-150 axis-mediated NF-κB pathway in LPS-challenged HUVECs and septic mice.Life Sci. 2021 Jan 15;265:118744. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118744. Epub 2020 Nov 9. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33181172
-
Paclitaxel alleviated liver injury of septic mice by alleviating inflammatory response via microRNA-27a/TAB3/NF-κB signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Jan;97:1424-1433. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.11.003. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29156532
-
MicroRNA-135a is up-regulated and aggravates myocardial depression in sepsis via regulating p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2017 Apr;45:6-12. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2017.01.029. Epub 2017 Jan 29. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28147298
-
MiR-324/SOCS3 Axis Protects Against Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-Induced Cardiomyocyte Injury and Regulates Myocardial Ischemia via TNF/NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Int Heart J. 2020 Nov 28;61(6):1258-1269. doi: 10.1536/ihj.19-687. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Int Heart J. 2020. PMID: 33191336
-
Inhibition of miR-155 alleviates sepsis-induced inflammation and intestinal barrier dysfunction by inactivating NF-κB signaling.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Jan;90:107218. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107218. Epub 2020 Dec 6. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33296782
Cited by
-
High Mobility Group Proteins in Sepsis.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 2;13:911152. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.911152. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35720285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs and Sepsis-Induced Cardiac Dysfunction: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 30;22(1):321. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010321. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33396834 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of MicroRNAs in Sepsis-Related Organ Dysfunction: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 19;23(16):9354. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169354. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012630 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory Role of Non-Coding RNAs on Immune Responses During Sepsis.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 9;12:798713. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.798713. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34956235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deletion of TLR4 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver injury by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021 Oct;42(10):1610-1619. doi: 10.1038/s41401-020-00597-x. Epub 2021 Jan 25. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021. PMID: 33495514 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Crit Care Med. 2017;45(3):486–552. - PubMed
-
- Li Z, Gao M, Yang B, et al. Naringin attenuates MLC phosphorylation and NF-kappaB activation to protect sepsis-induced intestinal injury via RhoA/ROCK pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;103:50–58. - PubMed
-
- Weng L, Zeng X-Y, Yin P, et al. Sepsis-related mortality in China: a descriptive analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2018;44(7):1071–1080. - PubMed
-
- Deutschman CS, Tracey KJ.. Sepsis: current dogma and new perspectives. Immunity. 2014;40(4):463–475. - PubMed
-
- Cohen J, Vincent J-L, Adhikari NKJ, et al. Sepsis: a roadmap for future research. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15(5):581–614. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
