Performance of neural network basecalling tools for Oxford Nanopore sequencing
- PMID: 31234903
- PMCID: PMC6591954
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-019-1727-y
Performance of neural network basecalling tools for Oxford Nanopore sequencing
Abstract
Background: Basecalling, the computational process of translating raw electrical signal to nucleotide sequence, is of critical importance to the sequencing platforms produced by Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT). Here, we examine the performance of different basecalling tools, looking at accuracy at the level of bases within individual reads and at majority-rule consensus basecalls in an assembly. We also investigate some additional aspects of basecalling: training using a taxon-specific dataset, using a larger neural network model and improving consensus basecalls in an assembly by additional signal-level analysis with Nanopolish.
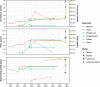
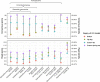
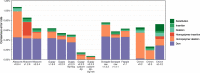
Results: Training basecallers on taxon-specific data results in a significant boost in consensus accuracy, mostly due to the reduction of errors in methylation motifs. A larger neural network is able to improve both read and consensus accuracy, but at a cost to speed. Improving consensus sequences ('polishing') with Nanopolish somewhat negates the accuracy differences in basecallers, but pre-polish accuracy does have an effect on post-polish accuracy.
Conclusions: Basecalling accuracy has seen significant improvements over the last 2 years. The current version of ONT's Guppy basecaller performs well overall, with good accuracy and fast performance. If higher accuracy is required, users should consider producing a custom model using a larger neural network and/or training data from the same species.
Keywords: Basecalling; Long-read sequencing; Oxford Nanopore.
Conflict of interest statement
In July 2018, Ryan Wick attended a hackathon in Bermuda at ONT’s expense. ONT also paid his travel, accommodation and registration to attend the London Calling (2017) and Nanopore Community Meeting (2017) events as an invited speaker.
Figures

References
-
- Charalampous T, Richardson H, Kay GL, Baldan R, Jeanes C, Rae D, Grundy S, Turner DJ, Wain J, Leggett RM, Livermore DM, O’Grady J. Rapid diagnosis of lower respiratory infection using Nanopore-based clinical metagenomics. bioRxiv. 2018:387548. 10.1101/387548.
-
- Graves A, Fernández S, Gomez F, Schmidhuber J. Connectionist temporal classification: Labelling unsegmented sequence data with recurrent neural networks. In: ICML ’06 Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning: 2006. p. 369–76. 10.1145/1143844.1143891. http://arxiv.org/abs/1607.03597.
-
- Stoiber M, Brown J. BasecRAWller: Streaming nanopore basecalling directly from raw signal. bioRxiv. 2017:1–15. 10.1101/133058.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

