Epiregulin reprograms cancer-associated fibroblasts and facilitates oral squamous cell carcinoma invasion via JAK2-STAT3 pathway
- PMID: 31234944
- PMCID: PMC6591968
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-019-1277-x
Epiregulin reprograms cancer-associated fibroblasts and facilitates oral squamous cell carcinoma invasion via JAK2-STAT3 pathway
Abstract
Background: Local resident normal fibroblasts (NFs) are the major source of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), which are distinguishable from NFs by their tumor-supportive properties. However, the mechanism and the effects underlying the transition of NFs to CAFs in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) remain unclear.
Methods: Five pairs of matching primary NFs and CAFs derived from OSCC patients were sent for RNA sequencing. Epiregulin (EREG) expression was analyzed by IHC in fibroblasts from OSCC patients. The role of EREG in the NF-CAF transition and the consequential effects on OSCC progression were examined by upregulation/downregulation of EREG in NFs/CAFs both in vitro and in vivo.
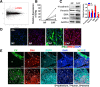
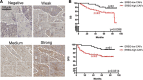
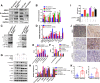
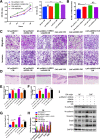
Results: Here, we identified epiregulin (EREG) as the most remarkably upregulated gene in CAFs. High EREG expression in CAFs correlated with higher T stage, deeper invasion and inferior worst pattern of invasion (WPOI) in OSCC patients and predicted shorter overall survival. Overexpression of EREG in NFs activated the CAF phenotype. Mechanistically, the JAK2/STAT3 pathway was enhanced by EREG in parallel with increased IL-6 expression, which could be inhibited by the JAK2 inhibitor AG490. Recombinant IL-6 upregulated the JAK2/STAT3/EREG pathway in a feedback loop. Moreover, EREG-induced CAF activation promoted the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) necessary for migration and invasion, which was dependent on JAK2/STAT3 signaling and IL-6. In vivo, EREG expression in stroma fibroblasts promoted tumor growth with high stromal α-SMA, phospho-JAK2/STAT3, and IL-6 expression and upregulated EMT in HSC3 cells.
Conclusions: EREG is essential for the NF-CAF transformation needed to induce EMT of tumor cells in a JAK2-STAT3- and IL-6-dependent manner in OSCC.
Keywords: Cancer-associated fibroblasts; Epiregulin; Invasion; Metastasis; Oral squamous cell carcinoma; Transition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IL-6 secreted by cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of gastric cancer via JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway.Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 28;8(13):20741-20750. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15119. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28186964 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaluronan synthase 2 expressed by cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes oral cancer invasion.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Nov 25;35(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0458-0. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27884164 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer-associated fibroblasts-derived exosomal piR-35462 promotes the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma via FTO/Twist1 pathway.BMC Oral Health. 2025 May 28;25(1):840. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-06082-3. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40437442 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Challenges and opportunities.Int J Cancer. 2021 Apr 1;148(7):1548-1561. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33352. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Int J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33091960 Review.
-
Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Heterogeneity in Malignancy with Focus on Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 21;25(2):1300. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021300. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38279300 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IL-33/ST2 signaling promotes constitutive and inductive PD-L1 expression and immune escape in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Br J Cancer. 2023 Mar;128(5):833-843. doi: 10.1038/s41416-022-02090-0. Epub 2022 Dec 3. Br J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36463324 Free PMC article.
-
IGF2BP2 promotes cell invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition through Src-mediated upregulation of EREG in oral cancer.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Jan 1;20(3):818-830. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.91786. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38250159 Free PMC article.
-
The multifaceted role of STAT3 pathway and its implication as a potential therapeutic target in oral cancer.Arch Pharm Res. 2022 Aug;45(8):507-534. doi: 10.1007/s12272-022-01398-y. Epub 2022 Aug 20. Arch Pharm Res. 2022. PMID: 35987863 Review.
-
Exploring the multifaceted role of direct interaction between cancer cells and fibroblasts in cancer progression.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 May 28;11:1379971. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1379971. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38863965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of integrin subunit genes in pancreatic cancer and the construction of a prognosis model.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Oct 31;15(5):2286-2304. doi: 10.21037/jgo-24-612. Epub 2024 Oct 29. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39554585 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81772880/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81702680/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- YKK16164/Nanjing Medical Science and Technique Development Foundation
- QRX17083/Nanjing Medical Science and Technique Development Foundation
- since 2017/Jiangsu Provincial Key Medical Discipline
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

