The Effects of Morphine, Baclofen, and Buspirone Alone and in Combination on Schedule-Controlled Responding and Hot Plate Antinociception in Rats
- PMID: 31235534
- PMCID: PMC6697778
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.118.255844
The Effects of Morphine, Baclofen, and Buspirone Alone and in Combination on Schedule-Controlled Responding and Hot Plate Antinociception in Rats
Abstract
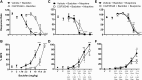
Better therapeutic options are needed for pain. Baclofen, buspirone, and morphine are characterized as having analgesic properties. However, little is known about potential interactions between analgesic effects of these drugs when combined. Furthermore, it is not known if the magnitude of these potential interactions will be similar for all drug effects. Thus, we tested the effects of these drugs alone and in combination for their capacity to produce thermal antinociception and to decrease food-maintained responding. Four male and four female Sprague-Dawley rats responded for food under a fixed-ratio 10 schedule; afterward they were immediately placed on a 52°C hot plate. Morphine, baclofen, and buspirone were examined alone and in 1:1 combinations, based upon ED50 values. Morphine and baclofen effects were evaluated with the opioid antagonist naltrexone and the GABAB antagonist (3-Aminopropyl)(diethoxymethyl)phosphinic acid (CGP35348), respectively. Morphine, baclofen, and buspirone dose dependently decreased operant responding, with the calculated ED50 values being 7.09, 3.42, and 0.57 mg/kg, respectively. The respective antinociception ED50 values were 16.15, 8.75, and 2.20 mg/kg. Analysis of 1:1 combinations showed the effects of morphine plus baclofen to decrease schedule-controlled responding and to produce thermal antinociception were synergistic. Effects of morphine plus buspirone and baclofen plus buspirone to decrease schedule-controlled responding were additive. Effects of the two combinations to produce thermal antinociception were synergistic. Naltrexone and CGP35348 antagonized the effects of morphine and baclofen, respectively. Synergistic antinociceptive effects, in conjunction with additive effects on food-maintained responding, highlight the therapeutic utility of opioid and non-opioid drug combinations.
Copyright © 2019 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The effects of mitragynine and morphine on schedule-controlled responding and antinociception in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Sep;236(9):2725-2734. doi: 10.1007/s00213-019-05247-7. Epub 2019 May 17. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 31098655 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of intracerebroventricular injection of GABA receptor agents on morphine-induced antinociception in the formalin test.J Psychopharmacol. 2002 Mar;16(1):85-91. doi: 10.1177/026988110201600108. J Psychopharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11949777
-
GABA(B) receptor mechanism and imipramine-induced antinociception in ligated and non-ligated mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2000 Oct 27;407(1-2):65-72. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(00)00648-8. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 11050292
-
Effects of gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) on schedule-controlled responding in rats: role of GHB and GABAB receptors.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004 Jan;308(1):182-8. doi: 10.1124/jpet.103.058909. Epub 2003 Oct 20. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004. PMID: 14569056
-
Effect of a selective GABA(B) receptor agonist baclofen on the mu-opioid receptor agonist-induced antinociceptive, emetic and rewarding effects.Neuropharmacology. 2005 Dec;49(8):1121-31. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2005.06.009. Epub 2005 Aug 10. Neuropharmacology. 2005. PMID: 16095635
Cited by
-
Potentially Life-Threatening Interaction between Opioids and Intrathecal Baclofen in Individuals with a Childhood-Onset Neurological Disorder: A Case Series and Review of the Literature.Neuropediatrics. 2024 Oct;55(5):294-302. doi: 10.1055/s-0044-1787103. Epub 2024 May 22. Neuropediatrics. 2024. PMID: 38776978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cannabidiol and mitragynine exhibit differential interactive effects in the attenuation of paclitaxel-induced mechanical allodynia, acute antinociception, and schedule-controlled responding in mice.Pharmacol Rep. 2023 Aug;75(4):937-950. doi: 10.1007/s43440-023-00498-w. Epub 2023 May 27. Pharmacol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37243887
-
Interactive Effects of µ-Opioid and Adrenergic-α 2 Receptor Agonists in Rats: Pharmacological Investigation of the Primary Kratom Alkaloid Mitragynine and Its Metabolite 7-Hydroxymitragynine.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2022 Dec;383(3):182-198. doi: 10.1124/jpet.122.001192. Epub 2022 Sep 24. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2022. PMID: 36153006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Leo JA, Tawfik VL, LaCroix-Fralish ML. (2006) The tetrapartite synapse: path to CNS sensitization and chronic pain. Pain 122:17–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

