Nogo-A targeted therapy promotes vascular repair and functional recovery following stroke
- PMID: 31235580
- PMCID: PMC6628809
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1905309116
Nogo-A targeted therapy promotes vascular repair and functional recovery following stroke
Abstract
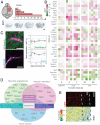
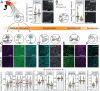
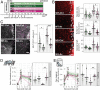
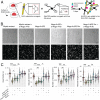
Stroke is a major cause of serious disability due to the brain's limited capacity to regenerate damaged tissue and neuronal circuits. After ischemic injury, a multiphasic degenerative and inflammatory response is coupled with severely restricted vascular and neuronal repair, resulting in permanent functional deficits. Although clinical evidence indicates that revascularization of the ischemic brain regions is crucial for functional recovery, no therapeutics that promote angiogenesis after cerebral stroke are currently available. Besides vascular growth factors, guidance molecules have been identified to regulate aspects of angiogenesis in the central nervous system (CNS) and may provide targets for therapeutic angiogenesis. In this study, we demonstrate that genetic deletion of the neurite outgrowth inhibitor Nogo-A or one of its corresponding receptors, S1PR2, improves vascular sprouting and repair and reduces neurological deficits after cerebral ischemia in mice. These findings were reproduced in a therapeutic approach using intrathecal anti-Nogo-A antibodies; such a therapy is currently in clinical testing for spinal cord injury. These results provide a basis for a therapeutic blockage of inhibitory guidance molecules to improve vascular and neural repair after ischemic CNS injuries.
Keywords: CNS; guidance factor; ischemia; revascularization; therapeutic angiogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: M.E.S. is a founder and board member of the University of Zurich spin-off company NovaGo Therapeutics Inc., seeking to develop antibody-based therapies for neurological diseases.
Figures



References
-
- Feigin V. L., et al. ; Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries and Risk Factors Study 2013 and Stroke Experts Writing Group , Global burden of stroke and risk factors in 188 countries, during 1990-2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet Neurol. 15, 913–924 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Henderson R. D., Eliasziw M., Fox A. J., Rothwell P. M., Barnett H. J.; North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial (NASCET) Group , Angiographically defined collateral circulation and risk of stroke in patients with severe carotid artery stenosis. Stroke 31, 128–132 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Krupinski J., Kaluza J., Kumar P., Kumar S., Wang J. M., Role of angiogenesis in patients with cerebral ischemic stroke. Stroke 25, 1794–1798 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Hayashi T., Noshita N., Sugawara T., Chan P. H., Temporal profile of angiogenesis and expression of related genes in the brain after ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 23, 166–180 (2003). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

