Impact of AKI on Urinary Protein Excretion: Analysis of Two Prospective Cohorts
- PMID: 31235617
- PMCID: PMC6622423
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2018101036
Impact of AKI on Urinary Protein Excretion: Analysis of Two Prospective Cohorts
Abstract
Background: Prior studies of adverse renal consequences of AKI have almost exclusively focused on eGFR changes. Less is known about potential effects of AKI on proteinuria, although proteinuria is perhaps the strongest risk factor for future loss of renal function.
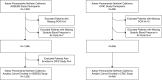
Methods: We studied enrollees from the Assessment, Serial Evaluation, and Subsequent Sequelae of AKI (ASSESS-AKI) study and the subset of the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) study enrollees recruited from Kaiser Permanente Northern California. Both prospective cohort studies included annual ascertainment of urine protein-to-creatinine ratio, eGFR, BP, and medication use. For hospitalized participants, we used inpatient serum creatinine measurements obtained as part of clinical care to define an episode of AKI (i.e., peak/nadir inpatient serum creatinine ≥1.5). We performed mixed effects regression to examine change in log-transformed urine protein-to-creatinine ratio after AKI, controlling for time-updated covariates.
Results: At cohort entry, median eGFR was 62.9 ml/min per 1.73 m2 (interquartile range [IQR], 46.9-84.6) among 2048 eligible participants, and median urine protein-to-creatinine ratio was 0.12 g/g (IQR, 0.07-0.25). After enrollment, 324 participants experienced at least one episode of hospitalized AKI during 9271 person-years of follow-up; 50.3% of first AKI episodes were Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes stage 1 in severity, 23.8% were stage 2, and 25.9% were stage 3. In multivariable analysis, an episode of hospitalized AKI was independently associated with a 9% increase in the urine protein-to-creatinine ratio.
Conclusions: Our analysis of data from two prospective cohort studies found that hospitalization for an AKI episode was independently associated with subsequent worsening of proteinuria.
Keywords: acute renal failure; proteinuria; renal injury.
Copyright © 2019 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

References
-
- Hsu CY: Yes, AKI truly leads to CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol 23: 967–969, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group : KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl 3: 1–150, 2013
-
- Remuzzi G, Bertani T: Pathophysiology of progressive nephropathies. N Engl J Med 339: 1448–1456, 1998 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000424/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK114014/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072231/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK098233/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061021/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060963/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK100468/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK082192/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CIHR/Canada
- UL1 TR000003/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK084012/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061028/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK082183/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK082223/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DK111881/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002548/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK060990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060980/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK082185/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK101507/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM104940/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR013987/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016500/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM109036/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002003/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061022/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000433/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029879/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

