Genome-wide analysis of dental caries and periodontitis combining clinical and self-reported data
- PMID: 31235808
- PMCID: PMC6591304
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-10630-1
Genome-wide analysis of dental caries and periodontitis combining clinical and self-reported data
Abstract
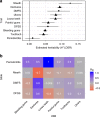
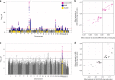
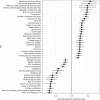
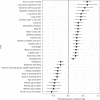
Dental caries and periodontitis account for a vast burden of morbidity and healthcare spending, yet their genetic basis remains largely uncharacterized. Here, we identify self-reported dental disease proxies which have similar underlying genetic contributions to clinical disease measures and then combine these in a genome-wide association study meta-analysis, identifying 47 novel and conditionally-independent risk loci for dental caries. We show that the heritability of dental caries is enriched for conserved genomic regions and partially overlapping with a range of complex traits including smoking, education, personality traits and metabolic measures. Using cardio-metabolic traits as an example in Mendelian randomization analysis, we estimate causal relationships and provide evidence suggesting that the processes contributing to dental caries may have undesirable downstream effects on health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collabarators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390:1211–1259. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32154-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- Dnr 2011-3372/Vetenskapsrådet (Swedish Research Council)/International
- K23 DE026804/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- L30 DE028110/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE014899/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK116074/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 202802/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- C18281/A19169/Cancer Research UK (CRUK)/International
- 2015-02597/Vetenskapsrådet (Swedish Research Council)/International
- MC_PC_15018/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 DE018903/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DE025046/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- G9815508/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 4.1-2016-00416/Vetenskapsrådet (Swedish Research Council)/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

