Alteration of the IL-33-sST2 pathway in hypertensive patients and a mouse model
- PMID: 31235844
- PMCID: PMC8075887
- DOI: 10.1038/s41440-019-0291-x
Alteration of the IL-33-sST2 pathway in hypertensive patients and a mouse model
Abstract
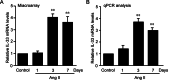
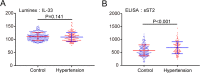
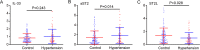
Inflammatory cells play an important role in the occurrence of hypertension. Recent studies have demonstrated that interleukin-33/suppression of tumorigenicity 2 (IL-33/ST2) signaling plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of several cardiovascular diseases. We aimed to evaluate the association of IL-33 and its receptor levels with the occurrence of hypertension in angiotensin II (Ang II)-infused mice using microarray analysis and validated our results in human specimens. Male wild-type mice were infused with Ang II (1500 ng/kg/min) for 1, 3 and 7 days. Patients with essential hypertension (EH) (n = 166) and healthy control subjects (n = 306) were enrolled. Levels of IL-33 and ST2 mRNAs in serum and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were analyzed by Luminex assay or ELISA and qPCR analysis. We found that IL-33 expression was significantly increased in the aortas of mice receiving Ang II infusion compared with that of control mice. In contrast, the levels of IL-33 in serum and PBMCs were not significantly different between hypertensive patients and normal controls. However, the levels of soluble ST2 (sST2) in serum and PBMCs were markedly higher in hypertensive patients than in controls (P < 0.001 and P = 0.014, respectively). In addition, the ST2L level in PBMCs was also significantly decreased in hypertensive patients (P = 0.028). Further, logistic analysis showed that the odds ratios of having hypertension based on sST2 levels in serum and PBMCs were 9.714 and 2.244 (P = 0.013 and P = 0.024, respectively) compared with the control group. Above all, sST2 acted as a risk factor for the occurrence of hypertension and may be a promising novel predictive marker for EH.
Keywords: Hypertension; IL-33; Peripheral blood mononuclear cells; ST2L; sST2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rodriguez-Iturbe B, Pons H, Quiroz Y, Lanaspa MA, Johnson RJ. Autoimmunity in the pathogenesis of hypertension. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014;10:56–62. - PubMed
-
- Wang L, Zhang YL, Lin QY, Liu Y, Guan XM, Ma XL, et al. CXCL1-CXCR2 axis mediates angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy and remodelling through regulation of monocyte infiltration. Eur Heart J. 2018;39:1818–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

