Effects of early enteral nutrition on Th17/Treg cells and IL-23/IL-17 in septic patients
- PMID: 31236002
- PMCID: PMC6580355
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i22.2799
Effects of early enteral nutrition on Th17/Treg cells and IL-23/IL-17 in septic patients
Abstract
Background: The imbalance of Th17/Treg cells and the IL-23/IL-17 axis have been confirmed to be associated with sepsis and various inflammatory diseases. Early enteral nutrition (EEN) can modulate the inflammatory response, improve immune dysfunction, and prevent enterogenic infection in critically ill patients; however, the precise mechanisms remain unclear. Considering the important roles of Th17 and Treg lymphocytes in the development of inflammatory and infectious diseases, we hypothesized that EEN could improve the immune dysfunction in sepsis by maintaining a balanced Th17/Treg cell ratio and by regulating the IL-23/IL-17 axis.
Aim: To investigate the effects of EEN on the Th17/Treg cell ratios and the IL-23/IL-17 axis in septic patients.
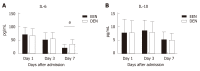
Methods: In this prospective clinical trial, patients were randomly divided into an EEN or delayed enteral nutrition (DEN) group. Enteral feeding was started within 48 h in the EEN group, whereas enteral feeding was started on the 4th day in the DEN group. The Th17 and Treg cell percentages and the interleukin levels were tested on days 1, 3, and 7 after admission. The clinical severity and outcome variables were also recorded.
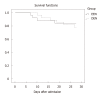
Results: Fifty-three patients were enrolled in this trial from October 2017 to June 2018. The Th17 cell percentages, Th17/Treg cell ratios, IL-17, IL-23, and IL-6 levels of the EEN group were lower than those of the DEN group on the 7th day after admission (P < 0.05). The duration of mechanical ventilation and of the intensive care unit stay of the EEN group were shorter than those of the DEN group (P < 0.05). However, no difference in the 28-d mortality was found between the two groups (P = 0.728).
Conclusion: EEN could regulate the imbalance of Th17/Treg cell ratios and suppress the IL-23/IL-17 axis during sepsis. Moreover, EEN could reduce the clinical severity of sepsis but did not reduce the 28-d mortality of septic patients.
Keywords: Early enteral nutrition; Enteral nutrition; IL-23/IL-17 axis; Sepsis; T helper lymphocytes; Th17/Treg cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

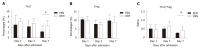

Similar articles
-
Effects of early enteral nutrition on T helper lymphocytes of surgical septic patients: A retrospective observational study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Aug;96(32):e7702. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007702. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28796054 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Early Enteral Nutrition on Immune Function and Prognosis of Patients With Sepsis on Mechanical Ventilation.J Intensive Care Med. 2020 Oct;35(10):1053-1061. doi: 10.1177/0885066618809893. Epub 2018 Nov 1. J Intensive Care Med. 2020. PMID: 30384813
-
Effects of early enteral nutrition on immune function of severe acute pancreatitis patients.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Feb 14;19(6):917-22. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i6.917. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23431120 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
T helper 17 cell/regulatory T-cell imbalance in hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa: the link to hair follicle dissection, obesity, smoking and autoimmune comorbidities.Br J Dermatol. 2018 Aug;179(2):260-272. doi: 10.1111/bjd.16561. Epub 2018 Jun 11. Br J Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 29573406 Review.
-
Impact of early enteral nutrition in critically ill children: A systematic review and meta-analysis.JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2025 May;49(4):428-440. doi: 10.1002/jpen.2738. Epub 2025 Feb 19. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39972677
Cited by
-
Heparin-binding protein as a biomarker of gastrointestinal dysfunction in critically ill patients: a retrospective cross-sectional study in China.BMJ Open. 2020 Jul 5;10(7):e036396. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-036396. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 32624474 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory T Cells: Angels or Demons in the Pathophysiology of Sepsis?Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 25;13:829210. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.829210. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35281010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenesis and Treatment of Cytokine Storm Induced by Infectious Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 30;22(23):13009. doi: 10.3390/ijms222313009. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrin αEβ7 is involved in the intestinal barrier injury of sepsis.Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Jan 18;14(2):780-788. doi: 10.18632/aging.203839. Epub 2022 Jan 18. Aging (Albany NY). 2022. PMID: 35042191 Free PMC article.
-
The beneficial effects of neutrophil elastase inhibitor on gastrointestinal dysfunction in sepsis.Clin Transl Sci. 2024 May;17(5):e13829. doi: 10.1111/cts.13829. Clin Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 38769746 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gupta DL, Bhoi S, Mohan T, Galwnkar S, Rao DN. Coexistence of Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg imbalances in patients with post traumatic sepsis. Cytokine. 2016;88:214–221. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Li M, Su L, Wang H, Xiao K, Deng J, Jia Y, Han G, Xie L. Alterations of T helper lymphocyte subpopulations in sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock: A prospective observational study. Inflammation. 2015;38:995–1002. - PubMed
-
- Feng P, Yan R, Dai X, Xie X, Wen H, Yang S. The alteration and clinical significance of Th1/Th2/Th17/Treg cells in patients with multiple myeloma. Inflammation. 2015;38:705–709. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Feng Y, Shen X, Pan G, Fan G, Gao X, Han J, Zhu Y. Anti-sepsis protection of Xuebijing injection is mediated by differential regulation of pro- and anti-inflammatory Th17 and T regulatory cells in a murine model of polymicrobial sepsis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018;211:358–365. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

