Efficacy and Safety of Xiao Ai Ping Injection Combined with Chemotherapy in Advanced Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 31236124
- PMCID: PMC6545757
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/3821053
Efficacy and Safety of Xiao Ai Ping Injection Combined with Chemotherapy in Advanced Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Xiao Ai Ping injection (XAPI), extracted from the Chinese herbal medicine Marsdenia tenacissima, is widely used in the adjuvant treatment of tumors in China. The present study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of XAPI combined with chemotherapy for treating patients with advanced gastric cancer. Seven databases were searched for relevant studies published up to October 1, 2018, and Review Manager 5.3 software and Stata 12.0 software were used for meta-analysis. Fourteen studies, representing 1097 enrolled patients, were included in our analysis. Compared with chemotherapy alone, combination treatment with XAPI and the XELOX regimen (capecitabine plus oxaliplatin) was found to improve the objective response rate (ORR) [RR=1.36; 95%CI (1.10, 1.70); P=0.006], disease control rate (DCR) [RR=1.15; 95% CI (1.04, 1.28); P=0.010], and Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS) improvement rate [RR=1.51; 95%CI (1.14, 2.00); P=0.004] and to reduce the incidence of leukopenia [RR=0.68; 95%CI (0.55,0.84); P=0.0005], liver damage [RR=0.59; 95% CI (0.37, 0.92); P=0.02], renal impairment [RR=0.39; 95% CI (0.18, 0.85); P=0.02], and hand-foot syndrome [RR=0.56; 95%CI (0.35,0.90); P=0.02]. However, median progression-free survival (PFS), 1-year survival rate, and median overall survival (OS) were not extended by XAPI plus XELOX. Combination treatment with XAPI and the SOX regimen (tegafur plus oxaliplatin) did not improve ORR or DCR, but it did enhance the KPS improvement rate [RR=1.73; 95%CI (1.23,2.43); P=0.002] and reduce the incidence of nausea and vomiting [RR=0.66; 95% CI (0.50, 0.88); P=0.004]. XAPI in combination with the FOLFOX regimen (fluorouracil/calcium folinate/oxaliplatin) enhanced only the KPS improvement rate [RR=1.68; 95%CI (1.18,2.39); P=0.004] and had no significant effect on ORR or DCR or the incidence of adverse events. A single study reported that XAPI combined with the CPT-11 regimen (irinotecan) was superior to chemotherapy alone with respect to DCR and also reduced the incidence of leukopenia, liver damage, and hand-foot syndrome during chemotherapy, while prolonging PFS. Finally, one study reported that XAPI combined with the TP regimen (palitaxel plus cisplatin) improved ORR and KPS improvement rate to a greater extent than TP alone. Although the present review has some limitations, the findings suggest that XAPI combined with chemotherapy may represent a beneficial treatment strategy, particularly the combination of XAPI and XELOX.
Figures




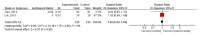
Similar articles
-
Oral and injectable Marsdenia tenacissima extract (MTE) as adjuvant therapy to chemotherapy for gastric cancer: a systematic review.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019 Dec 12;19(1):366. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2779-y. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019. PMID: 31830977 Free PMC article.
-
Xiao-ai-ping injection adjunct with platinum-based chemotherapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020 Jan 13;20(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2795-y. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020. PMID: 32020869 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Compound Kushen Injection for Advanced Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials with Trial Sequential Analysis.Integr Cancer Ther. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15347354241258458. doi: 10.1177/15347354241258458. Integr Cancer Ther. 2024. PMID: 38853681 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese herbal medicine combined with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of contributions of specific medicinal materials to tumor response.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 25;13:977708. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.977708. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36091754 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of Xiao-ai-ping injection add-on therapy to chemotherapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Oct 6;102(40):e35483. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035483. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37800773 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Oral and injectable Marsdenia tenacissima extract (MTE) as adjuvant therapy to chemotherapy for gastric cancer: a systematic review.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019 Dec 12;19(1):366. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2779-y. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019. PMID: 31830977 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering the molecular mechanism of Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Thunb.) Makino against breast cancer using network pharmacology and molecular docking.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Dec 9;101(49):e32165. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032165. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36626523 Free PMC article.
-
Marsdenia tenacissima Extract Induces Autophagy and Apoptosis of Hepatocellular Cells via MIF/mToR Signaling.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Mar 4;2022:7354700. doi: 10.1155/2022/7354700. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35280512 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese Herbal Medicine and Its Regulatory Effects on Tumor Related T Cells.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Apr 21;11:492. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00492. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32372963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Bioinformatics Research on Novel Mechanism of Compound Kushen Injection for Treating Breast Cancer by Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Verification.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Aug 10;2020:2758640. doi: 10.1155/2020/2758640. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32849897 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hess L. M., Michael D., Mytelka D. S., Beyrer J., Liepa A. M., Nicol S. Chemotherapy treatment patterns, costs, and outcomes of patients with gastric cancer in the United States: a retrospective analysis of electronic medical record (EMR) and administrative claims data. Gastric Cancer. 2016;19(2):607–615. doi: 10.1007/s10120-015-0486-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

