Eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2 and human digestive system neoplasms
- PMID: 31236196
- PMCID: PMC6580320
- DOI: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i6.449
Eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2 and human digestive system neoplasms
Abstract
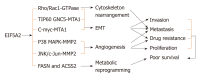
Eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2 (eIF5A2), as one of the two isoforms in the family, is reported to be a novel oncogenic protein that is involved in multiple aspects of many types of human cancer. Overexpression or gene amplification of EIF5A2 has been demonstrated in many cancers. Accumulated evidence shows that eIF5A2 initiates tumor formation, enhances cancer cell growth, increases cancer cell metastasis, and promotes treatment resistance through multiple means, including inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition, cytoskeletal rearrangement, angiogenesis, and metabolic reprogramming. Expression of eIF5A2 in cancer correlates with poor survival, advanced disease stage, as well as metastasis, suggesting that eIF5A2 function is crucial for tumor development and maintenance but not for normal tissue homeostasis. All these studies suggest that eIF5A2 is a useful biomarker in the prediction of cancer prognosis and serves as an anticancer molecular target. This review focuses on the expression, subcellular localization, post-translational modifications, and regulatory networks of eIF5A2, as well as its biochemical functions and evolving clinical applications in cancer, especially in human digestive system neoplasms.
Keywords: Acetylation modification; Cancer therapeutics; Drug resistance; Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2; Hypusine modification.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: There are no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Roles of eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2 in human cancer.Int J Biol Sci. 2013 Oct 12;9(10):1013-20. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.7191. eCollection 2013. Int J Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24250246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpression of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 (EIF5A2) correlates with cell aggressiveness and poor survival in gastric cancer.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 20;10(3):e0119229. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119229. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25793713 Free PMC article.
-
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 promotes metabolic reprogramming in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Carcinogenesis. 2017 Jan;38(1):94-104. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgw119. Epub 2016 Nov 22. Carcinogenesis. 2017. PMID: 27879277
-
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 (eIF5A2) regulates chemoresistance in colorectal cancer through epithelial mesenchymal transition.Cancer Cell Int. 2015 Nov 17;15:109. doi: 10.1186/s12935-015-0250-9. eCollection 2015. Cancer Cell Int. 2015. PMID: 26581310 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling EIF5A2: A multifaceted player in cellular regulation, tumorigenesis and drug resistance.Eur J Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 15;997:177596. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.177596. Epub 2025 Apr 5. Eur J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40194645 Review.
Cited by
-
eIF5B regulates the expression of PD-L1 in prostate cancer cells by interacting with Wig1.BMC Cancer. 2021 Sep 15;21(1):1022. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08749-w. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34525951 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of MicroRNAs in Chemoresistance to Cisplatin in the Top Five Deadliest Cancer: An Updated Review.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 4;13:831099. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.831099. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35444536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long Noncoding RNA TP73-AS1 Modulates Medulloblastoma Progression In Vitro And In Vivo By Sponging miR-494-3p And Targeting EIF5A2.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Nov 18;12:9873-9885. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S228305. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31819485 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting eIF5A2 inhibits prostate carcinogenesis, migration, invasion and metastasis in vitro and in vivo.Bioengineered. 2020 Jan 1;11(1):619-627. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2020.1774993. Bioengineered. 2020. PMID: 32522053 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of EIF5A2 is associated with poor survival and aggressive tumor biology in gallbladder cancer.Histol Histopathol. 2020 Jun;35(6):579-587. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-186. Epub 2019 Nov 20. Histol Histopathol. 2020. PMID: 31745968
References
-
- Jenkins ZA, Hååg PG, Johansson HE. Human eIF5A2 on chromosome 3q25-q27 is a phylogenetically conserved vertebrate variant of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A with tissue-specific expression. Genomics. 2001;71:101–109. - PubMed
-
- Guan XY, Sham JS, Tang TC, Fang Y, Huo KK, Yang JM. Isolation of a novel candidate oncogene within a frequently amplified region at 3q26 in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2001;61:3806–3809. - PubMed
-
- Clement PM, Henderson CA, Jenkins ZA, Smit-McBride Z, Wolff EC, Hershey JW, Park MH, Johansson HE. Identification and characterization of eukaryotic initiation factor 5A-2. Eur J Biochem. 2003;270:4254–4263. - PubMed
-
- Yang SS, Gao Y, Wang DY, Xia BR, Liu YD, Qin Y, Ning XM, Li GY, Hao LX, Xiao M, Zhang YY. Overexpression of eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2 (EIF5A2) is associated with cancer progression and poor prognosis in patients with early-stage cervical cancer. Histopathology. 2016;69:276–287. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

