The efficacy and safety of besifloxacin for acute bacterial conjunctivitis: a Meta-analysis
- PMID: 31236364
- PMCID: PMC6580202
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2019.06.24
The efficacy and safety of besifloxacin for acute bacterial conjunctivitis: a Meta-analysis
Retraction in
-
Retraction Notice.Int J Ophthalmol. 2019 Sep 18;12(9):1401. eCollection 2019. Int J Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31544033 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the relative efficacy and safety of besifloxacin for treatment of acute bacterial conjunctivitis.
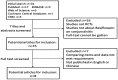
Methods: A comprehensive search in PubMed, EMBASE Web of Science, Cochrane Central Database and CNKI was undertaken for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing besifloxacin with other treatments or placebo. The primary outcome measures were clinical resolution, rates of bacterial eradication, individual clinical outcomes, cure rates, and bacterial eradication rates of different kinds of pathogens. Safety outcomes were the number of adverse effects (AEs). The final search was performed on August 2018.
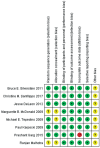
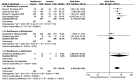
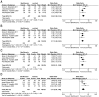
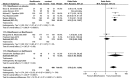
Results: Eight RCTs were included. Five studies compared the efficacy and safety of besifloxacin with placebo, 2 studies compared besifloxacin with moxifloxacin, and 1 study compared besifloxacin with gatifloxacin. A total of 3105 patients met the inclusion criteria. Besifloxacin presented higher efficacy and safety than did placebo in clinical resolution, rates of bacterial eradication, individual clinical outcomes, cure rates, bacterial eradication rates of different kinds of pathogens and the number of AEs. There was no significant difference between besifloxacin and moxifloxacin or gatifloxacin in the comparison items mentioned above.
Conclusion: Besifloxacin is highly effective and safe for treatment of acute bacterial conjunctivitis. Further comparative trials regarding the effect of besifloxacin for treatment of acute bacterial conjunctivitis will aid in treatment decisions.
Keywords: Meta-analysis; acute bacterial conjunctivitis; besifloxacin; randomized controlled trials.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Treating with besifloxacin for acute bacterial conjunctivitis: a Meta-analysis.Int J Ophthalmol. 2019 Dec 18;12(12):1898-1907. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2019.12.13. eCollection 2019. Int J Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31850176 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of besifloxacin ophthalmic suspension 0.6% compared with moxifloxacin ophthalmic solution 0.5% for treating bacterial conjunctivitis.Ophthalmology. 2009 Sep;116(9):1615-1623.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2009.05.014. Epub 2009 Jul 29. Ophthalmology. 2009. PMID: 19643483 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of besifloxacin ophthalmic suspension 0.6% in children and adolescents with bacterial conjunctivitis: a post hoc, subgroup analysis of three randomized, double-masked, parallel-group, multicenter clinical trials.Paediatr Drugs. 2010 Apr 1;12(2):105-12. doi: 10.2165/11534380-000000000-00000. Paediatr Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20218747
-
The role of besifloxacin in the treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis.Ann Pharmacother. 2014 May;48(5):616-25. doi: 10.1177/1060028014524175. Epub 2014 Feb 24. Ann Pharmacother. 2014. PMID: 24566460 Review.
-
Besifloxacin: a topical fluoroquinolone for the treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis.Clin Ther. 2010 Mar;32(3):454-71. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.03.013. Clin Ther. 2010. PMID: 20399984 Review.
References
-
- Sheikh A, Hurwitz B, van Schayck CP, McLean S, Nurmatov U. Antibiotics versus placebo for acute bacterial conjunctivitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;(9):CD001211. - PubMed
-
- Alfonso SA, Fawley JD, Alexa Lu X. Conjunctivitis. Prim Care. 2015;42(3):325–345. - PubMed
-
- Chikviladze D, Nikuradze N, Gachechiladze Kh, Miqeladze M, Metreveli D. Microbial structure of acute bacterial conjunctivitis. Georgian Med News. 2013;(216):12–15. - PubMed
-
- Høvding G. Acute bacterial conjunctivitis. Acta Ophthalmol. 2008;86(1):5–17. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
