Safety, efficacy and tumor mutational burden as a biomarker of overall survival benefit in chemo-refractory gastric cancer treated with toripalimab, a PD-1 antibody in phase Ib/II clinical trial NCT02915432
- PMID: 31236579
- PMCID: PMC6771223
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdz197
Safety, efficacy and tumor mutational burden as a biomarker of overall survival benefit in chemo-refractory gastric cancer treated with toripalimab, a PD-1 antibody in phase Ib/II clinical trial NCT02915432
Abstract
Background: High tumor mutational burden (TMB-H) is correlated with enhanced objective response rate (ORR) and progression-free survival (PFS) for certain cancers receiving immunotherapy. This study aimed to investigate the safety and efficacy of toripalimab, a humanized programmed death-1 (PD-1) antibody, in advanced gastric cancer (AGC), and the predictive survival benefit of TMB and PD-L1.
Patients and methods: We reported on the AGC cohort of phase Ib/II trial evaluating the safety and activity of toripalimab in patients with AGC, oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. In cohort 1, 58 chemo-refractory AGC patients received toripalimab (3 mg/kg d1, Q2W) as a monotherapy. In cohort 2, 18 chemotherapy-naive AGC patients received toripalimab (360 mg d1, Q3W) with oxaliplatin 130 mg/m2 qd, d1, capecitabine 1000 mg/m2 b.i.d., d1-d14, Q3W as first-line treatment. Primary end point was ORR. Biomarkers such as PD-L1 and TMB were evaluated for correlation with clinical efficacy.
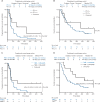
Results: In cohort 1, the ORR was 12.1% and the disease control rate (DCR) was 39.7%. Median PFS was 1.9 months and median OS was 4.8 months. The TMB-H group showed significant superior OS than the TMB-L group [14.6 versus 4.0 months, HR = 0.48 (96% CI 0.24-0.96), P = 0.038], while PD-L1 overexpression did not correlate with significant survival benefit. A 77.6% of patients experienced at least one treatment-related adverse event (TRAE), and 22.4% of patients experienced a grade 3 or higher TRAE. In cohort 2, the ORR was 66.7% and the DCR was 88.9%. A 94.4% of patients experienced at least one TRAE and 38.9% of patients experienced grade 3 or higher TRAEs.
Conclusions: Toripalimab has demonstrated a manageable safety profile and promising antitumor activity in AGC patients, especially in combination with XELOX. High TMB may be a predictive marker for OS of AGC patients receiving toripalimab as a single agent.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02915432.
Keywords: gastric cancer; immunotherapy; programmed death ligand-1; tumor mutational burden.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society for Medical Oncology.
Figures



Comment in
-
Tumor mutational burden as a new biomarker for PD-1 antibody treatment in gastric cancer.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2019 Nov 14;39(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s40880-019-0417-1. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2019. PMID: 31727167 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Safety and efficacy of toripalimab in advanced gastric cancer: A new clinical trial bringing hope for immunotherapy in gastric cancer.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2020 Apr;40(4):194-196. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12019. Epub 2020 Apr 11. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32277740 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD. et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 2016; 66(2): 115–132. - PubMed
-
- Kim JM, Chen DS.. Immune escape to PD-L1/PD-1 blockade: seven steps to success (or failure). Ann Oncol 2016; 27(8): 1492–1504. - PubMed
-
- Muro K, Chung HC, Shankaran V. et al. Pembrolizumab for patients with PD-L1-positive advanced gastric cancer (KEYNOTE-012): a multicentre, open-label, phase 1b trial. Lancet Oncol 2016; 17(6): 717–726. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

