Circadian rhythm of activin A and related parameters of mineral metabolism in normal and uremic rats
- PMID: 31236663
- PMCID: PMC6614158
- DOI: 10.1007/s00424-019-02291-2
Circadian rhythm of activin A and related parameters of mineral metabolism in normal and uremic rats
Abstract
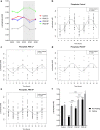
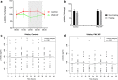
Activin A is a new fascinating player in chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD), which is implicated in progressive renal disease, vascular calcification, and osteodystrophy. Plasma activin A rises early in the progression of renal disease. Disruption of circadian rhythms is related to increased risk of several diseases and circadian rhythms are observed in mineral homeostasis, bone parameters, and plasma levels of phosphate and PTH. Therefore, we examined the circadian rhythm of activin A and CKD-MBD-related parameters (phosphate, PTH, FGF23, and klotho) in healthy controls and CKD rats (5/6 nephrectomy) on high-, standard- and low-dietary phosphate contents as well as during fasting conditions. Plasma activin A exhibited circadian rhythmicity in healthy control rats with fourfold higher values at acrophase compared with nadir. The rhythm was obliterated in CKD. Activin A was higher in CKD rats compared with controls when measured at daytime but not significantly when measured at evening/nighttime, stressing the importance of time-specific reference intervals when interpreting plasma values. Plasma phosphate, PTH, and FGF23 all showed circadian rhythms in control rats, which were abolished or disrupted in CKD. Plasma klotho did not show circadian rhythm. Thus, the present investigation shows, for the first time, circadian rhythm of plasma activin A. The rhythmicity is severely disturbed by CKD and is associated with disturbed rhythms of phosphate and phosphate-regulating hormones PTH and FGF23, indicating that disturbed circadian rhythmicity is an important feature of CKD-MBD.
Keywords: Activin A; CKD; Circadian rhythm; FGF23; Klotho; Phosphate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
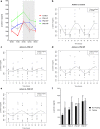
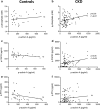
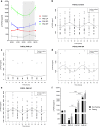
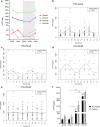
Comment in
-
The rhythm of healthy kidneys.Pflugers Arch. 2019 Sep;471(9):1159-1160. doi: 10.1007/s00424-019-02297-w. Epub 2019 Jul 12. Pflugers Arch. 2019. PMID: 31300871 No abstract available.
References
-
- Anastasilakis AD, Polyzos SA, Makras P, Gkiomisi A, Savvides M, Papatheodorou A, Terpos E. Circulating activin-a is elevated in postmenopausal women with low bone mass: the three-month effect of zoledronic acid treatment. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24:2127–2132. doi: 10.1007/s00198-012-2198-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barker SL, Pastor J, Carranza D, Quinones H, Griffith C, Goetz R, Mohammadi M, Ye J, Zhang J, Hu MC, Kuro-o M, Moe OW, Sidhu SS. The demonstration of alphaKlotho deficiency in human chronic kidney disease with a novel synthetic antibody. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2015;30:223–233. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfu291. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

