A case report on endarteritis in a child with coarctation of aorta
- PMID: 31237036
- PMCID: PMC6771818
- DOI: 10.1111/echo.14418
A case report on endarteritis in a child with coarctation of aorta
Abstract
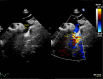
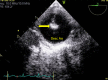
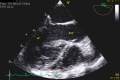
Coarctation of aorta(CoA), complicated by endarteritis in a children is very rare. Here we present a case of endarteritis in an unoperated CoA in a four year old boy. CoA had been diagnosed in the referring hospital, yet the diagnosis of endocarditis distal to CoA, was made in the tertiary center using modified transthoracic echo windows or focused views. After six weeks of intravenous antibiotic treatment, a coarctectomy and end-to-end anastomosis was performed and he recovered clinically well. This case report concludes that echocardiography remains as the standard diagnostic method for identifying intracardiac manifestations of infective endocarditis/endarteritis. Last but foremost, it delineates the importance of modified transthoracic echo windows or focused views in identifying the unusual position of endocarditis.
Keywords: Streptococcus sanguinius; coarctation of aorta; congenital heart disease; endarteritis; infective endocarditis.
© 2019 The Authors. Echocardiography Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Franco‐Paredes C, Workowski K, Harris M. Infective endocarditis‐endarteritis complicating coarctation of the aorta. Am J Med. 2002;112(7):590–592. - PubMed
-
- Anderson AM, Cabell CH, Sexton DJ. Aortic coarctation endarteritis in an adult: case report with cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging findings and review of the literature. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;40(4):e28–e31. - PubMed
-
- Rodbard S. Blood velocity and endocarditis. Circulation. 1963;27:18–28. - PubMed
-
- Leininger CR. Coarctation of the aorta, with superimposed bacterial endarteritis. Am J Dis Child. 1946;72:238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

