A robust circadian rhythm of metabolites in Arabidopsis thaliana mutants with enhanced growth characteristics
- PMID: 31237908
- PMCID: PMC6592530
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218219
A robust circadian rhythm of metabolites in Arabidopsis thaliana mutants with enhanced growth characteristics
Abstract
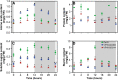
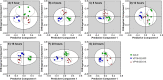
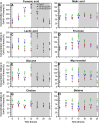
Climate change and the rising food demand provide a need for smart crops that yield more biomass. Recently, two Arabidopsis thaliana mutants with enhanced growth characteristics, VP16-02-003 and the VP16-05-014, were obtained by genome-wide reprogramming of gene expression, which led to the identification of novel biomarkers of these enhanced growth phenotypes. Since the circadian cycle strongly influences metabolic and physiological processes and exerts control over the photosynthetic machinery responsible for enhanced growth, in this study, we investigate the influences of the circadian clock on the metabolic rhythm of eighteen key biomarkers for the larger rosette surface area phenotype. The metabolic profile was studied in intact leaves at seven different time points throughout the circadian cycle using high-resolution magic angle spinning (HR-MAS) NMR. The results show that the circadian rhythm of biomarker metabolites are remarkably robust across wild-type Col-0 and VP16-02-003 and the VP16-05-014 mutants, with widely different metabolite levels of both mutants compared to Col-0 throughout the circadian cycle. Our analysis reveals that robustness is achieved through functional independence between the circadian clock and primary metabolic processes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Mba C, Guimaraes EP, Ghosh K. Re-orienting crop improvement for the changing climatic conditions of the 21st century. Agriculture & Food Security. BioMed Central; 2012;1: 7–17.
-
- Kumar A, Pathak RK, Gupta SM, Gaur VS, Pandey D. Systems Biology for Smart Crops and Agricultural Innovation: Filling the Gaps between Genotype and Phenotype for Complex Traits Linked with Robust Agricultural Productivity and Sustainability. OMICS. 2015;19: 581–601. 10.1089/omi.2015.0106 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kamburova VS, Nikitina EV, Shermatov SE, Buriev ZT, Kumpatla SP, Emani C, et al. Genome Editing in Plants: An Overview of Tools and Applications. International Journal of Agronomy. 2017;2017: 15 10.1155/2017/7315351 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

