A Low-Cost, Wireless, 3-D-Printed Custom Armband for sEMG Hand Gesture Recognition
- PMID: 31238529
- PMCID: PMC6631507
- DOI: 10.3390/s19122811
A Low-Cost, Wireless, 3-D-Printed Custom Armband for sEMG Hand Gesture Recognition
Abstract
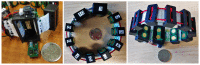
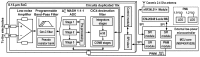
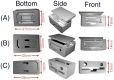
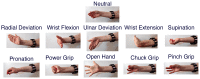
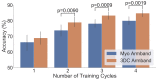
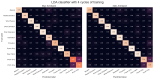
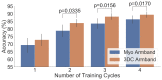
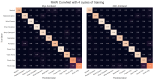
Wearable technology can be employed to elevate the abilities of humans to perform demanding and complex tasks more efficiently. Armbands capable of surface electromyography (sEMG) are attractive and noninvasive devices from which human intent can be derived by leveraging machine learning. However, the sEMG acquisition systems currently available tend to be prohibitively costly for personal use or sacrifice wearability or signal quality to be more affordable. This work introduces the 3DC Armband designed by the Biomedical Microsystems Laboratory in Laval University; a wireless, 10-channel, 1000 sps, dry-electrode, low-cost (∼150 USD) myoelectric armband that also includes a 9-axis inertial measurement unit. The proposed system is compared with the Myo Armband by Thalmic Labs, one of the most popular sEMG acquisition systems. The comparison is made by employing a new offline dataset featuring 22 able-bodied participants performing eleven hand/wrist gestures while wearing the two armbands simultaneously. The 3DC Armband systematically and significantly ( p < 0.05 ) outperforms the Myo Armband, with three different classifiers employing three different input modalities when using ten seconds or more of training data per gesture. This new dataset, alongside the source code, Altium project and 3-D models are made readily available for download within a Github repository.
Keywords: acquisition system; gesture recognition; sEMG; surface electromyogram; wearable sensors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of the data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
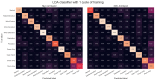

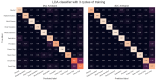


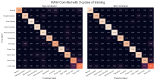

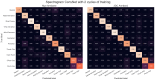








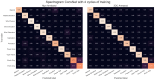
References
-
- Hakonen M., Piitulainen H., Visala A. Current state of digital signal processing in myoelectric interfaces and related applications. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2015;18:334–359. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2015.02.009. - DOI
-
- Allard U.C., Nougarou F., Fall C.L., Giguère P., Gosselin C., Laviolette F., Gosselin B. A convolutional neural network for robotic arm guidance using semg based frequency-features; Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS); Daejeon, Korea. 9–14 October 2016; pp. 2464–2470.
-
- Janke M., Diener L. Emg-to-speech: Direct generation of speech from facial electromyographic signals. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2017;25:2375–2385. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2017.2738568. - DOI
-
- Oskoei M.A., Hu H. Myoelectric control systems—A survey. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2007;2:275–294. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2007.07.009. - DOI
-
- Stegeman D.F., Kleine B.U., Lapatki B.G., Van Dijk J.P. High-density surface EMG: Techniques and applications at a motor unit level. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2012;32:3–27.

