Research Progress of Near-Infrared Fluorescence Immunoassay
- PMID: 31238547
- PMCID: PMC6630960
- DOI: 10.3390/mi10060422
Research Progress of Near-Infrared Fluorescence Immunoassay
Abstract
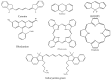
Near-infrared fluorescence probes (NIFPs) have been widely used in immunoassay, bio-imaging and medical diagnosis. We review the basic principles of near-infrared fluorescence and near-infrared detection technology, and summarize structures, properties and characteristics of NIFPs (i.e., cyanines, xanthenes fluorescent dyes, phthalocyanines, porphyrin derivates, single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs), quantum dots and rare earth compounds). We next analyze applications of NIFPs in immunoassays, and prospect the application potential of lateral flow assay (LFA) in rapid detection of pathogens. At present, our team intends to establish a new platform that has highly sensitive NIFPs combined with portable and simple immunochromatographic test strips (ICTSs) for rapid detection of food-borne viruses. This will provide technical support for rapid detection on the port.
Keywords: immunoassay; immunochromatographic test strips (ICTSs); near-infrared fluorescence probes (NIFPs); pathogen detection; quantum dots; rare earth compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Diao S., Hong G.S., Antaris A.L., Blackburn J.L., Chen K., Cheng Z., Dai H.J. Biological imaging without autofluorescence in the second near-infared region. Nano Res. 2015;8:3027–3034. doi: 10.1007/s12274-015-0808-9. - DOI
-
- Hong G.S., Antaris A.L., Dai H.J. Near-infrared fluorophores for biomedical imaging. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017;1:0010. doi: 10.1038/s41551-016-0010. - DOI
-
- Reineck P., Gibson B.C. Near-infrared fluorescent nano-materials for bioimaging and sensing. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2017;5:1–26.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

