Preparation of cooperative RNA recognition complexes for crystallographic structural studies
- PMID: 31239042
- PMCID: PMC6697268
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.mie.2019.04.001
Preparation of cooperative RNA recognition complexes for crystallographic structural studies
Abstract
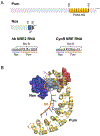
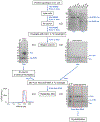
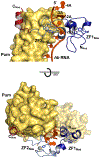
It is essential that mRNA-binding proteins recognize specific motifs in target mRNAs to control their processing, localization, and expression. Although mRNAs are typically targets of many different regulatory factors, our understanding of how they work together is limited. In some cases, RNA-binding proteins work cooperatively to regulate an mRNA target. A classic example is Drosophila melanogaster Pumilio (Pum) and Nanos (Nos). Pum is a sequence-specific RNA-binding protein. Nos also binds RNA, but interaction with some targets requires Pum to bind first. We recently determined crystal structures of complexes of Pum and Nos with two different target RNA sequences. A crystal structure in complex with the hunchback mRNA element showed how Pum and Nos together can recognize an extended RNA sequence with Nos binding to an A/U-rich sequence 5' of the Pum sequence element. Nos also enables recognition of elements that contain an A/U-rich 5' sequence, but imperfectly match the Pum sequence element. We determined a crystal structure of Pum and Nos in complex with the Cyclin B mRNA element, which demonstrated how Nos clamps the Pum-RNA complex and enables recognition of the imperfect element. Here, we describe methods for expression and purification of stable Pum-Nos-RNA complexes for crystallization, details of the crystallization and structure determination, and guidance on how to analyze protein-RNA structures and evaluate structure-driven hypotheses. We aim to provide tips and guidance that can be applied to other protein-RNA complexes. With hundreds of mRNA-binding proteins identified, combinatorial control is likely to be common, and much work remains to understand them structurally.
Keywords: Cooperative RNA binding; Nanos; PUF protein; Pumilio; X-ray crystallography.
2019 Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Drosophila Nanos acts as a molecular clamp that modulates the RNA-binding and repression activities of Pumilio.Elife. 2016 Aug 2;5:e17096. doi: 10.7554/eLife.17096. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27482653 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct RNA-binding modules in a single PUF protein cooperate to determine RNA specificity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Sep 19;47(16):8770-8784. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz583. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31294800 Free PMC article.
-
Significant roles in RNA-binding for the amino-terminal regions of Drosophila Pumilio and Nanos.PLoS Genet. 2025 Mar 31;21(3):e1011616. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011616. eCollection 2025 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2025. PMID: 40163518 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated structural biology to unravel molecular mechanisms of protein-RNA recognition.Methods. 2017 Apr 15;118-119:119-136. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2017.03.015. Epub 2017 Mar 16. Methods. 2017. PMID: 28315749 Review.
-
Engineered proteins with Pumilio/fem-3 mRNA binding factor scaffold to manipulate RNA metabolism.FEBS J. 2013 Aug;280(16):3755-67. doi: 10.1111/febs.12367. Epub 2013 Jun 24. FEBS J. 2013. PMID: 23731364 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkoczi G, Chen VB, Davis IW, Echols N, . . . Zwart PH (2010). PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallographica. Section D, Biological Crystallography, 66(Pt 2), 213–221. doi:10.1107/S0907444909052925 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barker DD, Wang C, Moore J, Dickinson LK, & Lehmann R (1992). Pumilio is essential for function but not for distribution of the Drosophila abdominal determinant Nanos. Genes & Development, 6(12A), 2312–2326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

