Power Doppler ultrasound and contrast-enhanced ultrasound demonstrate non-invasive tumour vascular response to anti-vascular therapy in canine cancer patients
- PMID: 31239493
- PMCID: PMC6592898
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-45682-2
Power Doppler ultrasound and contrast-enhanced ultrasound demonstrate non-invasive tumour vascular response to anti-vascular therapy in canine cancer patients
Abstract
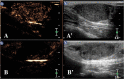
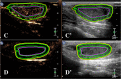
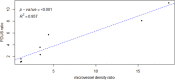
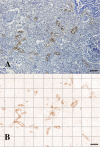
Combretastatin A4-phosphate (CA4P) is an anti-vascular agent which selectively shuts down blood supply in tumours, resulting in extensive tumour necrosis. The aim of this study was to assess in vivo, non-invasive ultrasound techniques for the early evaluation of tumour perfusion following CA4P treatment of spontaneous tumours. Eight dogs that bore spontaneous tumours were enrolled and were subsequently treated with a single dose of intravenous CA4P. Perfusion of tumours was evaluated by power Doppler ultrasound (PDUS) pre-treatment (0 h), during the injection (10 min, 20 min, 30 min) and after CA4P infusion (24 and 72 h). Vascularity index (VI) of the tumour tissue was quantitatively analysed and accuracy was verified by correlation analysis with the results of immunohistochemical evaluation of microvessel density (MVD). Central and peripheral perfusion was evaluated by contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) pre-treatment and at 72 h post-treatment. Post-treatment, PDUS demonstrated a significant decrease in VI within 10 min of CA4P infusion. CEUS parameters demonstrated a significant decrease in blood velocity and volume in the central aspect of the tumour. Histology revealed a 4.4-fold reduction (p < 0.001, 95% CI [2.2,9.4]) in MVD and a 4.1-fold increase (p = 0.003, 95% CI [1.4,11.8]) in necrotic tumour tissue. A strong correlation between PDUS results and immunohistochemical results was found (Pearson R2 = 0.957, p < 0.001). Furthermore, the findings of PDUS were supported by the objective results of the CEUS analyses. These data suggest a role for ultrasound in real-time, non-invasive monitoring of tumour vascular response as an early indicator of CA4P treatment efficacy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A single dose of intravenous combretastatin A4-phosphate is reasonably well tolerated and significantly reduces tumour vascularization in canine spontaneous cancers.Vet Comp Oncol. 2018 Dec;16(4):467-477. doi: 10.1111/vco.12402. Epub 2018 May 24. Vet Comp Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29797763
-
Quantitative Evaluation of Combretastatin A4 Phosphate Early Efficacy in a Tumor Model with Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2018 Apr;44(4):840-852. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2017.12.002. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29395676
-
Intra-individual comparison of therapeutic responses to vascular disrupting agent CA4P between rodent primary and secondary liver cancers.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Jul 7;24(25):2710-2721. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i25.2710. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29991876 Free PMC article.
-
Combretastatin A4 phosphate: a novel vascular disrupting agent.Future Oncol. 2010 Aug;6(8):1219-28. doi: 10.2217/fon.10.90. Future Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20799867 Review.
-
Combretastatin A4 phosphate.Anticancer Drugs. 2004 Mar;15(3):179-87. doi: 10.1097/00001813-200403000-00001. Anticancer Drugs. 2004. PMID: 15014350 Review.
Cited by
-
B-Mode and Doppler Ultrasonography in a Murine Model of Ehrlich Solid Carcinoma With Different Growth Patterns.Front Oncol. 2020 Nov 4;10:560413. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.560413. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33251133 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo, online label-free monitoring of heterogenous oxygen utilization during phototherapy with real-time ultrasound-guided photoacoustic imaging.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 3:2024.11.27.625759. doi: 10.1101/2024.11.27.625759. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39677615 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
B-Mode and Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasonography Aspects of Benign and Malignant Superficial Neoplasms in Dogs: A Preliminary Study.Animals (Basel). 2022 Oct 14;12(20):2765. doi: 10.3390/ani12202765. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290151 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical Applications of Multi-Platform Imaging in Animal Models of Cancer.Cancer Res. 2021 Mar 1;81(5):1189-1200. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-0373. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33262127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3-D Super-Resolution Ultrasound Imaging for Monitoring Early Changes in Breast Cancer after Treatment with a Vascular-Disrupting Agent.IEEE Int Ultrason Symp. 2021 Sep;2021:10.1109/IUS52206.2021.9593426. doi: 10.1109/IUS52206.2021.9593426. Epub 2021 Nov 12. IEEE Int Ultrason Symp. 2021. PMID: 38351971 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dark GG, et al. Combretastatin A-4, an agent that displays potent and selective toxicity toward tumor vasculature. Cancer Research. 1997;57:1829–1834. - PubMed
-
- Chaplin DJ, Pettit GR, Hill SA. Anti-vascular approaches to solid tumour therapy: evaluation of combretastatin A4 phosphate. Anticancer Research. 1999;19:189–196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

