Androgen receptor promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma cell migration by increasing EGFR phosphorylation
- PMID: 31239703
- PMCID: PMC6557262
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S200718
Androgen receptor promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma cell migration by increasing EGFR phosphorylation
Abstract
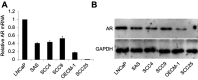
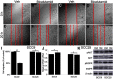
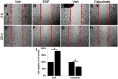
Objectives: This study is aimed to investigate the role of androgen receptor (AR) in regulating oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cells migration. Materials and methods: Tumors from 23 patients with OSCC and five OSCC cell lines were used for analyzing AR expression. The effects of AR agonist and antagonist were used to examine the role of AR in regulating the migration of OSCC cells. Results: Ten of 23 tumors from patients with OSCC were AR positive. There was no significant difference in total EGFR (tEGFR) expression between AR-positive tumors and AR-negative tumors. However, the expression of phosphorylated EGFR (pEGFR) in AR-positive tumors was significantly higher than that in AR-negative tumors (p<0.01). Stimulation of AR by dihydrotestosterone in SCC9 (AR-positive OSCC cell) caused an increase in pEGFR and pAKT expression and promoted cell migration without changed tEGFR expression, whereas treatment with bicalutamide led to a decrement in pEGFR expression and pAKT and inhibited cell migration. No effects were found in SCC25 cell line (AR-negative) either treated by dihydrotestosterone or bicalutamide. Furthermore, SCC9 cell line treated by EGF or cetuximab (EGFR inhibitor) significantly promoted or inhibited cell migration. Conclusion: Our data indicate that OSSC tumors and OSCC cell lines express AR which is critical for promoting cell migration by increasing EGFR phosphorylation.
Keywords: EGFR; androgen receptor; migration; oral squamous cell carcinoma; phosphorylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The oncogenic role of androgen receptors in promoting the growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells.Oral Dis. 2015 Apr;21(3):320-7. doi: 10.1111/odi.12272. Epub 2014 Aug 8. Oral Dis. 2015. PMID: 25040852
-
Dihydrotestosterone upregulates the expression of epidermal growth factor receptor and ERBB2 in androgen receptor-positive bladder cancer cells.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2011 Jul 4;18(4):451-64. doi: 10.1530/ERC-11-0010. Print 2011 Aug. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21613411
-
GALNT2 enhances migration and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma by regulating EGFR glycosylation and activity.Oral Oncol. 2014 May;50(5):478-84. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2014.02.003. Epub 2014 Feb 28. Oral Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24582885
-
Additive antitumor effects of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, gefitinib (Iressa), and the nonsteroidal antiandrogen, bicalutamide (Casodex), in prostate cancer cells in vitro.Int J Cancer. 2005 Jul 1;115(4):630-40. doi: 10.1002/ijc.20917. Int J Cancer. 2005. Retraction in: Int J Cancer. 2019 Jul 15;145(2):E12. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32130. PMID: 15700310 Retracted.
-
Expression of beta2-adrenergic receptor in oral squamous cell carcinoma.J Oral Pathol Med. 2009 Apr;38(4):371-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.2008.00691.x. Epub 2008 Dec 30. J Oral Pathol Med. 2009. PMID: 19141064
Cited by
-
The Effects of Androgens on T Cells: Clues to Female Predominance in Autoimmune Liver Diseases?Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 29;11:1567. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01567. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32849531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Potential Biomarkers Using Integrative Approach: A Case Study of ESCC.SN Comput Sci. 2023;4(2):114. doi: 10.1007/s42979-022-01492-4. Epub 2022 Dec 21. SN Comput Sci. 2023. PMID: 36573207 Free PMC article.
-
Biological roles and clinical significance of estrogen and androgen receptors in head and neck cancers.J Cancer. 2022 Apr 4;13(7):2189-2199. doi: 10.7150/jca.66707. eCollection 2022. J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35517428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anticancer Activity and Molecular Targets of Piper cernuum Substances in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Models.Biomedicines. 2023 Jul 6;11(7):1914. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11071914. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37509552 Free PMC article.
-
Jiawei Danxuan Koukang Alleviates Arecoline Induced Oral Mucosal Lesions: Network Pharmacology and the Combined Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC) and Mass Spectrometry (MS).Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023 Oct 13;17:3085-3101. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S413897. eCollection 2023. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023. PMID: 37854130 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

