Quorum quenching activity of Bacillus cereus isolate 30b confers antipathogenic effects in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 31239733
- PMCID: PMC6559722
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S182889
Quorum quenching activity of Bacillus cereus isolate 30b confers antipathogenic effects in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
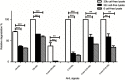
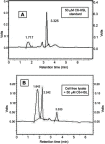
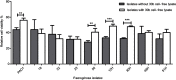
Background: Quorum quenching, the interference of a Quorum sensing (QS) system that contributes to the pathogenesis through triggering the production of various virulence determinants, is among the newly suggested antivirulence strategies. Purpose: This study aimed at screening of N-Acyl homoserine lactonase activity from local bacterial isolate, and investigating its effect on Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) virulence and biofilm formation. Materials and methods: Soil bacteria were screened for aiiA gene coding for lactonase enzyme by Polymerase Chain reaction and sequencing of aiiA gene homologs. Lactonase activity and spectrum were assessed in the cell-free lysate by well diffusion assay using Agrobacterium tumafaciens KYC55. A bacterial isolate showing the highest N-acyl-homoserine lactones degradation percentage was identified by gene amplification and sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene and its aiiA gene homolog. High performance liquid chromatography was used to confirm N-acyl-homoserine lactone degradation. The effect of cell-free lysate on the biofilm formation ability and cytotoxicity of P. aeruginosa PAO1 and P. aeruginosa clinical isolates from different clinical sources were assessed by static microtiter plate and viability assay, respectively Results: Lactonase gene and activity were identified in three Bacillus spp. isolates. They showed broad catalytic activities against tested N-acyl-homoserine lactones. However, The lactonase activity in the cell- free lysate of isolate 30b showed the highest significant degradation percentage on all tested signals; N-butanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (71%), N-hexanoyl-l-homoserine lactone (100%), N-decanoyl-homoserine lactone (100%), N-(3-oxohexanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone (37.5%), N-(oxodecanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone (100%), and N-(3-oxododecanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone (100%). Alignment of the amino acid sequences of AiiA protein of isolate 30b showed 96% identity with Bacillus cereus (B. cereus) homologous lactonases in the GenBank database, and the isolate was designated as B. cereus isolate 30b. Cell-free lysate of B. cereus isolate 30b reduced biofilm formation significantly in 93% of P. aeruginosa isolates. The highest mean percentage of reduction in the biofilm was 86%. Moreover, the viability percentage of human lung carcinoma A549 cells infected by P. aeruginosa and treated with cell-free lysate of B. cereus isolate 30b increased up to 15%. Conclusion: The results of this study highlight the potential of lactonases as a promising strategy to combat Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence.
Keywords: AHL; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; antivirulence; biofilm; cytotoxicity; lactonase; quorum quenching.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

