Fatty Liver and the Forensic Pathologist
- PMID: 31240043
- PMCID: PMC6490134
- DOI: 10.1177/1925362118782061
Fatty Liver and the Forensic Pathologist
Abstract
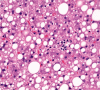
Fatty liver is a common finding in clinical practice and at autopsy. It is most commonly seen associated with alcohol abuse and in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). It may also be seen in many other conditions in both adults and children. It is now recognized that NAFLD, like alcoholic liver disease, may lead to end stage liver disease. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with increased mortality from other disorders, particularly cardiovascular diseases. Fatty liver may be seen in many conditions that concern autopsy pathologists, including drug toxicity, anorexia, hepatic ischemia, and heatstroke. In infants, steatosis is common in sudden unexpected deaths. Fatty liver has been associated with sudden death and this review examines the pathology and role of fatty liver in sudden death. Acad Forensic Pathol. 2018 8(2): 296-310.
Keywords: Alcohol; Fatty; Forensic pathology; Liver; NAFLD; Steatosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures & Declaration of Conflicts of Interest: Christopher M. Milroy is the Editor-In-Chief of Academic Forensic Pathology: The Official Publication of the National Association of Medical Examiners. The author, reviewers, editors, and publication staff do not report any other relevant conflicts of interest
Figures








References
-
- Tiniakos DG, Anstee QM, Burt AD. MacSween’s pathology of the liver. 7th ed Philadephia: Elsevier; c2018. Chapter 5, Fatty liver disease; p. 308–71.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
