Pregnancy outcome in Refsum disease: Affected fetuses and children born to an affected mother
- PMID: 31240149
- PMCID: PMC6498833
- DOI: 10.1002/jmd2.12020
Pregnancy outcome in Refsum disease: Affected fetuses and children born to an affected mother
Abstract
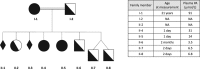
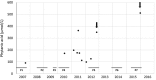
We describe the case of a young woman, from a consanguineous family, affected by adult Refsum disease (ARD, OMIM#266500). ARD is a rare peroxisomal autosomal recessive disease due to deficient alpha-oxidation of phytanic acid (PA), a branched-chain fatty acid. The accumulation of PA in organs is thought to be responsible for disease symptoms. The patient presented only bilateral shortening of metatarsals and has been treated with a low-PA diet. She is homoallelic for the c.135-2A > G mutation of PHYH, and she married her first cousin carrying the same mutation. She was pregnant seven times and had two homozygous girls. Due to a potential exacerbation of the disease during the third trimester of pregnancy, her weight and plasma PA levels were monitored. No specific events were noticed for the mother during the pregnancies and postpartum periods. This case also raised the question of potential exposure to PA (and its subsequent toxicity) of a homozygous fetus in a homozygous mother. Despite modestly elevated plasma concentrations of PA at birth (<30 μmol/L), the two affected girls did not present any specific sign of ARD and have so far developed normally. As only a few determinations of plasma PA levels in the mother could be performed during pregnancies, showing mild elevations (<350 μmol/L), it remains difficult to conclude as to a possible transplacental crossing of PA.
Keywords: Refsum disease; peroxisome; phytanic acid; pregnancy.
Conflict of interest statement
Patricia Dubot has accepted reimbursement for attending symposia from Sanofi‐Genzyme, Shire, Biomarin, or Orphan companies. Frédérique Sabourdy has accepted reimbursement for attending symposia from Sanofi‐Genzyme, Shire, Biomarin, or Orphan companies. Thierry Levade has accepted reimbursement for attending symposia from Sanofi‐Genzyme, Shire, Biomarin, or Orphan companies. Sandrine Roche has accepted reimbursement for attending symposia from Sanofi‐Genzyme, Shire, Biomarin, Nestlé, Biocodex, or Orphan companies. Guy Touati, Pierre Broué, Léonardo Astudillo, and Julien Baruteau declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Refsum S, Salomonsen L, Skatvedt M. Heredopathia atactica polyneuritiformis in children. J Pediatr. 1949;35:335‐343. - PubMed
-
- Klenk E, Kahike W. On the presence of 3,7,11,15‐tetramethylhexadecanoic acid (phytanic acid) in the cholesterol esters and other lipoid fractions of the organs in a case of a disease of unknown origin (possibly heredopathia atactica polyneuritiformis, Refsum's syndrome). Hoppe‐Seyler's Z Physiol Chem. 1963;333:133‐139. - PubMed
-
- Mize CE, Steinberg D, Avigan J, Fales HM. A pathway for oxidative degradation of phytanic acid in mammals. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966;25:359‐365. - PubMed
-
- Mihalik SJ, Rainville AM, Watkins PA. Phytanic acid α‐oxidation in rat liver peroxisomes. Eur J Biochem. 1995;232:545‐551. - PubMed
-
- Jansen GA, Hogenhout EM, Ferdinandusse S, et al. Human phytanoyl‐CoA hydroxylase: resolution of the gene structure and the molecular basis of Refsum's disease. Hum Mol Genet. 2000;9:1195‐1200. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials