MCRIP1 promotes the expression of lung-surfactant proteins in mice by disrupting CtBP-mediated epigenetic gene silencing
- PMID: 31240265
- PMCID: PMC6586819
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-019-0478-3
MCRIP1 promotes the expression of lung-surfactant proteins in mice by disrupting CtBP-mediated epigenetic gene silencing
Abstract
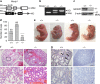
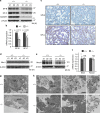
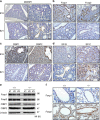
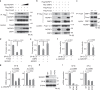
Proper regulation of epigenetic states of chromatin is crucial to achieve tissue-specific gene expression during embryogenesis. The lung-specific gene products, surfactant proteins B (SP-B) and C (SP-C), are synthesized in alveolar epithelial cells and prevent alveolar collapse. Epigenetic regulation of these surfactant proteins, however, remains unknown. Here we report that MCRIP1, a regulator of the CtBP transcriptional co-repressor, promotes the expression of SP-B and SP-C by preventing CtBP-mediated epigenetic gene silencing. Homozygous deficiency of Mcrip1 in mice causes fatal respiratory distress due to abnormal transcriptional repression of these surfactant proteins. We found that MCRIP1 interferes with interactions of CtBP with the lung-enriched transcriptional repressors, Foxp1 and Foxp2, thereby preventing the recruitment of the CtBP co-repressor complex to the SP-B and SP-C promoters and maintaining them in an active chromatin state. Our findings reveal a molecular mechanism by which cells prevent inadvertent gene silencing to ensure tissue-specific gene expression during organogenesis.
Keywords: Development; Differentiation; Gene silencing.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing financial or non-financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MCRIP1, an ERK substrate, mediates ERK-induced gene silencing during epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating the co-repressor CtBP.Mol Cell. 2015 Apr 2;58(1):35-46. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.01.023. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Mol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25728771
-
Brinker possesses multiple mechanisms for repression because its primary co-repressor, Groucho, may be unavailable in some cell types.Development. 2013 Oct;140(20):4256-65. doi: 10.1242/dev.099366. Development. 2013. PMID: 24086079 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-induced mitogenic factor modulates surfactant protein B and C expression in mouse lung.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006 Jan;34(1):28-38. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2005-0172OC. Epub 2005 Sep 15. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16166744 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-lipid interactions and surface activity in the pulmonary surfactant system.Chem Phys Lipids. 2006 Jun;141(1-2):105-18. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2006.02.017. Epub 2006 Mar 20. Chem Phys Lipids. 2006. PMID: 16600200 Review.
-
Transcriptional regulation by C-terminal binding proteins.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39(9):1593-607. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2007.01.025. Epub 2007 Feb 4. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17336131 Review.
Cited by
-
CtBP1 is essential for epigenetic silencing of μ-opioid receptor genes in the dorsal root ganglion in spinal nerve ligation-induced neuropathic pain.Neurotherapeutics. 2025 Jan;22(1):e00493. doi: 10.1016/j.neurot.2024.e00493. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Neurotherapeutics. 2025. PMID: 39580324 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of epigenetic regulators during lung development.Cell Death Dis. 2025 Jul 28;16(1):567. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07823-6. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 40721598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polycomb deficiency drives a FOXP2-high aggressive state targetable by epigenetic inhibitors.Nat Commun. 2023 Jan 20;14(1):336. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-35784-x. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36670102 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Expression of Mitosis and Cell Cycle Regulatory Genes during Recovery from an Acute Respiratory Virus Infection.Pathogens. 2021 Dec 15;10(12):1625. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10121625. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34959580 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy Is Required for Maturation of Surfactant-Containing Lamellar Bodies in the Lung and Swim Bladder.Cell Rep. 2020 Dec 8;33(10):108477. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108477. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 33296658 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

