Effects of the Angiotensin-Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor on Cardiac Reverse Remodeling: Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 31240976
- PMCID: PMC6662364
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012272
Effects of the Angiotensin-Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor on Cardiac Reverse Remodeling: Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background The angiotensin-receptor neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI) sacubitril/valsartan was shown to be superior to the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor enalapril in terms of reducing cardiovascular mortality in the PARADIGM-HF (Prospective Comparison of ARNI with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor to Determine Impact on Global Mortality and Morbidity in Heart Failure) study. However, the impact of ARNI on cardiac reverse remodeling (CRR) has not been established. Methods and Results We conducted a meta-analysis to compare the effects of ARNI versus angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers on CRR indices. We searched databases for studies published between 2010 and 2019 that reported CRR indices following ARNI administration. Effect size was expressed as mean difference (MD) with 95% CIs. Twenty studies enrolling 10 175 patients were included. ARNI improved functional capacity in patients with heart failure (HF) and a reduced ejection fraction (EF), including increasing New York Heart Association functional class (MD -0.79, 95% CI -0.86, -0.71) and 6-minute walking distance (MD 27.62 m, 95% CI 15.76, 39.48). ARNI outperformed angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin receptor blockers in terms of CRR indices, with striking changes in left ventricular EF, diameter, and volume. However, there were no significant improvements in indices except left ventricular mass index (MD -3.25 g/m2, 95% CI -3.78, -2.72) and left atrial volume (MD -7.20 mL, 95% CI -14.11, -0.29) in HF patients with preserved EF treated with ARNI. Improvements in CRR indices were observed at 3 months and became more significant with longer follow-up to 12 months. The regression equation for the relationship between left ventricular EF and end-diastolic dimension was y=0.041+0.071x+0.045x2+0.006x3. Conclusions ARNI distinctly improved left ventricular size and hypertrophy compared with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin receptor blockers in HF with reduced EF patients, even after short-term follow-up. Patients appeared to benefit more in terms of CRR treated with ARNI as early as possible and for at least 3 months. Further large sample trials are required to determine the effects of ARNI on CRR in HF with preserved EF patients.
Keywords: angiotensin‐receptor neprilysin inhibitor; cardiac reverse remodeling; end‐diastolic dimension; heart failure with a reduced ejection fraction; meta‐analysis.
Figures
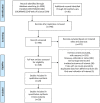


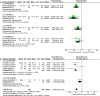
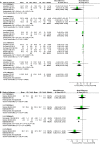

Similar articles
-
Influence of Ejection Fraction on Outcomes and Efficacy of Sacubitril/Valsartan (LCZ696) in Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: The Prospective Comparison of ARNI with ACEI to Determine Impact on Global Mortality and Morbidity in Heart Failure (PARADIGM-HF) Trial.Circ Heart Fail. 2016 Mar;9(3):e002744. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.115.002744. Circ Heart Fail. 2016. PMID: 26915374 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitors on left atrial remodeling and prognosis in heart failure.ESC Heart Fail. 2022 Feb;9(1):667-675. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.13691. Epub 2021 Nov 14. ESC Heart Fail. 2022. PMID: 34779134 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of Sacubitril/Valsartan and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors/Angiotensin Receptor Blockers in Patients With Reduced Ejection Fraction Combined With Moderate-to-Severe Chronic Kidney Disease.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2024 Jan-Dec;29:10742484241265337. doi: 10.1177/10742484241265337. Epub 2024 Jul 21. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2024. PMID: 39033432
-
Combined Angiotensin Receptor Antagonism and Neprilysin Inhibition.Circulation. 2016 Mar 15;133(11):1115-24. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.018622. Circulation. 2016. PMID: 26976916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Sacubitril/Valsartan, a First-in-Class, Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor (ARNI): Potential Uses in Hypertension, Heart Failure, and Beyond.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2018 Jan 27;20(1):5. doi: 10.1007/s11886-018-0944-4. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29374807 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and safety of sacubitril/valsartan vs. valsartan in patients with acute myocardial infarction: A meta-analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Aug 24;9:988117. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.988117. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36093128 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Sacubitril-Valsartan on Ventricular Arrhythmia Burden in Patients With Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction.Cureus. 2023 Feb 1;15(2):e34508. doi: 10.7759/cureus.34508. eCollection 2023 Feb. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 36874318 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Angiotensin-Neprilysin Versus Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibition on Renal Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 19;12:604017. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.604017. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34867310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Possible role of LCZ696 in atherosclerosis: new inroads and perspective.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Aug;479(8):1895-1908. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04816-x. Epub 2023 Aug 1. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37526794 Review.
-
The Inflammation-Fibrosis Combined Index: A Novel Marker for Predicting Left Ventricular Reverse Remodeling and Prognosis in Patients with HFrEF.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Jun 19;17:3967-3982. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S460641. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38915807 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Braunwald E. The war against heart failure: the Lancet lecture. Lancet. 2015;385:812–824. - PubMed
-
- Bhatt AS, Ambrosy AP, Velazquez EJ. Adverse remodeling and reverse remodeling after myocardial infarction. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2017;19:71. - PubMed
-
- Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, Bueno H, Cleland JG, Coats AJ, Falk V, González‐Juanatey JR, Harjola VP, Jankowska EA, Jessup M, Linde C, Nihoyannopoulos P, Parissis JT, Pieske B, Riley JP, Rosano GM, Ruilope LM, Ruschitzka F, Rutten FH, van der Meer P; Authors/Task Force Members; Document Reviewers . 2016 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur J Heart Fail. 2016;18:891–975. - PubMed
-
- White HD, Norris RM, Brown MA, Brandt PW, Whitlock RM, Wild CJ. Left ventricular end‐systolic volume as the major determinant of survival after recovery from myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1987;76:44–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

