Neural crest-specific deletion of Rbfox2 in mice leads to craniofacial abnormalities including cleft palate
- PMID: 31241461
- PMCID: PMC6663295
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.45418
Neural crest-specific deletion of Rbfox2 in mice leads to craniofacial abnormalities including cleft palate
Abstract
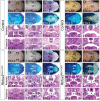
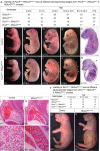
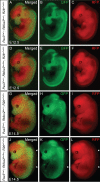
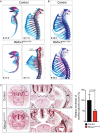
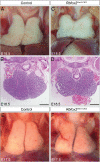
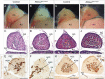
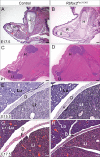
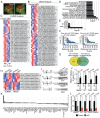
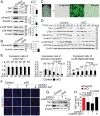
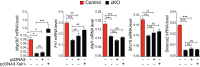
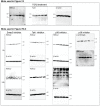
Alternative splicing (AS) creates proteomic diversity from a limited size genome by generating numerous transcripts from a single protein-coding gene. Tissue-specific regulators of AS are essential components of the gene regulatory network, required for normal cellular function, tissue patterning, and embryonic development. However, their cell-autonomous function in neural crest development has not been explored. Here, we demonstrate that splicing factor Rbfox2 is expressed in the neural crest cells (NCCs), and deletion of Rbfox2 in NCCs leads to cleft palate and defects in craniofacial bone development. RNA-Seq analysis revealed that Rbfox2 regulates splicing and expression of numerous genes essential for neural crest/craniofacial development. We demonstrate that Rbfox2-TGF-β-Tak1 signaling axis is deregulated by Rbfox2 deletion. Furthermore, restoration of TGF-β signaling by Tak1 overexpression can rescue the proliferation defect seen in Rbfox2 mutants. We also identified a positive feedback loop in which TGF-β signaling promotes expression of Rbfox2 in NCCs.
Keywords: Rbfox2; TGF-β signaling; Tak1; alternative splicing; cleft palate; developmental biology; mouse; neural crest.
© 2019, Cibi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
DC, MM, SG, LY, RS, PG, MH, LS, SG, MS No competing interests declared
Figures









References
-
- Bélanger C, Bérubé-Simard FA, Leduc E, Bernas G, Campeau PM, Lalani SR, Martin DM, Bielas S, Moccia A, Srivastava A, Silversides DW, Pilon N. Dysregulation of cotranscriptional alternative splicing underlies CHARGE syndrome. PNAS. 2018;115:E620–E629. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1715378115. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blonska M, Shambharkar PB, Kobayashi M, Zhang D, Sakurai H, Su B, Lin X. TAK1 is recruited to the tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) receptor 1 complex in a receptor-interacting protein (RIP)-dependent manner and cooperates with MEKK3 leading to NF-kappaB activation. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2005;280:43056–43063. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M507807200. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

