Cyclic vomiting syndrome: Pathophysiology, comorbidities, and future research directions
- PMID: 31241816
- PMCID: PMC6899706
- DOI: 10.1111/nmo.13607
Cyclic vomiting syndrome: Pathophysiology, comorbidities, and future research directions
Abstract
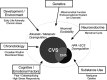
Cyclic vomiting syndrome (CVS) is characterized by severe episodic emesis in adults and children. Cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome is an increasingly recognized CVS-like illness that has been associated with chronic cannabis use. There are significant gaps in our understanding of the pathophysiology, clinical features, comorbidities, and effective management options of CVS. Recommendations for treating CVS are based on limited clinical data, as no placebo-controlled, randomized trials have yet been conducted. Diseases associated with CVS, including migraine, mitochondrial disorders, autonomic dysfunction, and psychiatric comorbidities, provide clues about pathophysiologic mechanisms and suggest potential therapies. We review our current understanding of CVS and propose future research directions with the aim of developing effective therapy. Establishing a multicenter, standardized registry of CVS patients could drive research on multiple fronts including developing CVS-specific outcome measures to broaden our understanding of clinical profiles, to serve as treatment end points in clinical trials, and to provide a platform for patient recruitment for randomized clinical trials. Such a robust database would also facilitate conduct of research that aims to determine the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms and genetic basis for CVS, as well as identifying potential biomarkers for the disorder. Soliciting government and industry support is crucial to establishing the necessary infrastructure and achieving these goals. Patient advocacy groups such as the Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome Association (CVSA), which partner with clinicians and researchers to disseminate new information, to promote ongoing interactions between patients, their families, clinicians, investigators, to support ongoing CVS research and education, must be an integral part of this endeavor.
Keywords: Cannabinoids; cyclic vomiting; migraine headaches; multicenter registry; psychosocial dysfunction.
© 2019 The Authors. Neurogastroenterology & Motility Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Tack J, Talley NJ, Camilleri M, et al. Functional gastroduodenal disorders. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:1466‐1479. - PubMed
-
- Stanghellini V, Chan FK, Hasler WL, et al. Rome IV ‐ gastroduodenal disorders. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:1380‐1392. - PubMed
-
- Sagar RC, Sood R, Gracie DJ, et al. Cyclic vomiting syndrome is a prevalent and under‐recognized condition in the gastroenterology outpatient clinic. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2018;30:e13174. - PubMed
-
- Basilisco G, Coletta M. Chronic constipation: a critical review. Dig Liver Dis. 2013;45:886‐893. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

