Airway Surface Liquid Has Innate Antiviral Activity That Is Reduced in Cystic Fibrosis
- PMID: 31242392
- PMCID: PMC6938132
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2018-0304OC
Airway Surface Liquid Has Innate Antiviral Activity That Is Reduced in Cystic Fibrosis
Abstract
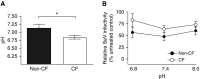
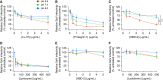
Although chronic bacterial infections and inflammation are associated with progressive lung disease in patients with cystic fibrosis (CF), much less is known regarding the contributions of respiratory viral infections to this process. Clinical studies suggest that antiviral host defenses may be compromised in individuals with CF, and CF airway epithelia exhibit impaired antiviral responses in vitro. Here, we used the CF pig model to test the hypothesis that the antiviral activity of respiratory secretions is reduced in CF. We developed an in vitro assay to measure the innate antiviral activity present in airway surface liquid (ASL) from CF and non-CF pigs. We found that tracheal and nasal ASL from newborn non-CF pigs exhibited dose-dependent inhibitory activity against several enveloped and encapsidated viruses, including Sendai virus, respiratory syncytial virus, influenza A, and adenovirus. Importantly, we found that the anti-Sendai virus activity of nasal ASL from newborn CF pigs was significantly diminished relative to non-CF littermate controls. This diminution of extracellular antiviral defenses appears to be driven, at least in part, by the differences in pH between CF and non-CF ASL. These data highlight the novel antiviral properties of native airway secretions and suggest the possibility that defects in extracellular antiviral defenses contribute to CF pathogenesis.
Keywords: airway secretions; airway surface liquid; antiviral proteins; cystic fibrosis; host defense.
Figures
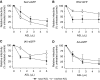
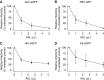
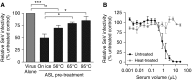
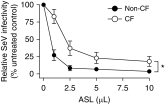
Comment in
-
Airway Surface Liquid and Impaired Antiviral Defense in Cystic Fibrosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2020 Jan;62(1):12-13. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2019-0239ED. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31348689 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Cohen-Cymberknoh M, Kerem E, Ferkol T, Elizur A. Airway inflammation in cystic fibrosis: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Thorax. 2013;68:1157–1162. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett J, McCray P. Cystic fibrosis and defective airway innate immunity. In: Hiemstra PS, Zaat SAJ, editors. Antimicrobial peptides and innate immunity. Basel, Switzerland: Springer Basel; 2013. pp. 275–306.
-
- Riordan JR, Rommens JM, Kerem B, Alon N, Rozmahel R, Grzelczak Z, et al. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989;245:1066–1073. - PubMed
-
- Rommens JM, Iannuzzi MC, Kerem B, Drumm ML, Melmer G, Dean M, et al. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: chromosome walking and jumping. Science. 1989;245:1059–1065. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

