Small Extracellular Vesicles Are Key Regulators of Non-cell Autonomous Intercellular Communication in Senescence via the Interferon Protein IFITM3
- PMID: 31242426
- PMCID: PMC6613042
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.05.095
Small Extracellular Vesicles Are Key Regulators of Non-cell Autonomous Intercellular Communication in Senescence via the Interferon Protein IFITM3
Abstract
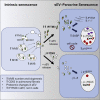
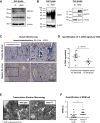
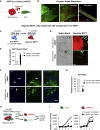
Senescence is a cellular phenotype present in health and disease, characterized by a stable cell-cycle arrest and an inflammatory response called senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). The SASP is important in influencing the behavior of neighboring cells and altering the microenvironment; yet, this role has been mainly attributed to soluble factors. Here, we show that both the soluble factors and small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) are capable of transmitting paracrine senescence to nearby cells. Analysis of individual cells internalizing sEVs, using a Cre-reporter system, show a positive correlation between sEV uptake and senescence activation. We find an increase in the number of multivesicular bodies during senescence in vivo. sEV protein characterization by mass spectrometry (MS) followed by a functional siRNA screen identify interferon-induced transmembrane protein 3 (IFITM3) as being partially responsible for transmitting senescence to normal cells. We find that sEVs contribute to paracrine senescence.
Keywords: DDIS; EV; IFITM3; OIS; aging; exosomes; fragilis; interferon; paracrine senescence; small extracellular vesicles.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Acosta J.C., O’Loghlen A., Banito A., Guijarro M.V., Augert A., Raguz S., Fumagalli M., Da Costa M., Brown C., Popov N. Chemokine signaling via the CXCR2 receptor reinforces senescence. Cell. 2008;133:1006–1018. - PubMed
- Acosta, J.C., O’Loghlen, A., Banito, A., Guijarro, M.V., Augert, A., Raguz, S., Fumagalli, M., Da Costa, M., Brown, C., Popov, N., et al. (2008). Chemokine signaling via the CXCR2 receptor reinforces senescence. Cell 133, 1006-1018. - PubMed
-
- Acosta J.C., Banito A., Wuestefeld T., Georgilis A., Janich P., Morton J.P., Athineos D., Kang T.W., Lasitschka F., Andrulis M. A complex secretory program orchestrated by the inflammasome controls paracrine senescence. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013;15:978–990. - PMC - PubMed
- Acosta, J.C., Banito, A., Wuestefeld, T., Georgilis, A., Janich, P., Morton, J.P., Athineos, D., Kang, T.W., Lasitschka, F., Andrulis, M., et al. (2013). A complex secretory program orchestrated by the inflammasome controls paracrine senescence. Nat. Cell Biol. 15, 978-990. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Caldwell M.E., DeNicola G.M., Martins C.P., Jacobetz M.A., Maitra A., Hruban R.H., Tuveson D.A. Cellular features of senescence during the evolution of human and murine ductal pancreatic cancer. Oncogene. 2012;31:1599–1608. - PMC - PubMed
- Caldwell, M.E., DeNicola, G.M., Martins, C.P., Jacobetz, M.A., Maitra, A., Hruban, R.H., and Tuveson, D.A. (2012). Cellular features of senescence during the evolution of human and murine ductal pancreatic cancer. Oncogene 31, 1599-1608. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cossetti C., Iraci N., Mercer T.R., Leonardi T., Alpi E., Drago D., Alfaro-Cervello C., Saini H.K., Davis M.P., Schaeffer J. Extracellular vesicles from neural stem cells transfer IFN-γ via Ifngr1 to activate Stat1 signaling in target cells. Mol. Cell. 2014;56:193–204. - PMC - PubMed
- Cossetti, C., Iraci, N., Mercer, T.R., Leonardi, T., Alpi, E., Drago, D., Alfaro-Cervello, C., Saini, H.K., Davis, M.P., Schaeffer, J., et al. (2014). Extracellular vesicles from neural stem cells transfer IFN-γ via Ifngr1 to activate Stat1 signaling in target cells. Mol. Cell 56, 193-204. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Demaria M., O’Leary M.N., Chang J., Shao L., Liu S., Alimirah F., Koenig K., Le C., Mitin N., Deal A.M. Cellular Senescence Promotes Adverse Effects of Chemotherapy and Cancer Relapse. Cancer Discov. 2017;7:165–176. - PMC - PubMed
- Demaria, M., O’Leary, M.N., Chang, J., Shao, L., Liu, S., Alimirah, F., Koenig, K., Le, C., Mitin, N., Deal, A.M., et al. (2017). Cellular Senescence Promotes Adverse Effects of Chemotherapy and Cancer Relapse. Cancer Discov. 7, 165-176. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

